Multiple Instance Spanning-Tree Operation
Loop Protection
Loop Protection
In cases where spanning tree cannot be used to prevent loops at the edge of
the network, loop protection may provide a suitable alternative. Unlike
spanning tree, however, loop protection is not a comprehensive loop detection
feature and should only be enabled on untagged edge ports, that is, ports that
connect to unmanaged switches and/or clients at the edge of the network.
The cases where loop protection might be chosen ahead of spanning tree to
detect and prevent loops are as follows:
■ On ports with client authentication. When spanning tree is enabled
on a switch that use 802.1X, Web authentication, and MAC authentication,
loops may go undetected. For example, spanning tree packets that are
looped back to an edge port will not be processed because they have a
different broadcast/multicast MAC address from the client-authenticated
MAC address. To ensure that client-authenticated edge ports get blocked
when loops occur, you should enable loop protection on those ports.
■ On ports connected to unmanaged devices. Spanning tree cannot
detect the formation of loops where there is an unmanaged device on the
network that does not process spanning tree packets and simply drops
them. Loop protection has no such limitation, and can be used to prevent
loops on unmanaged switches.
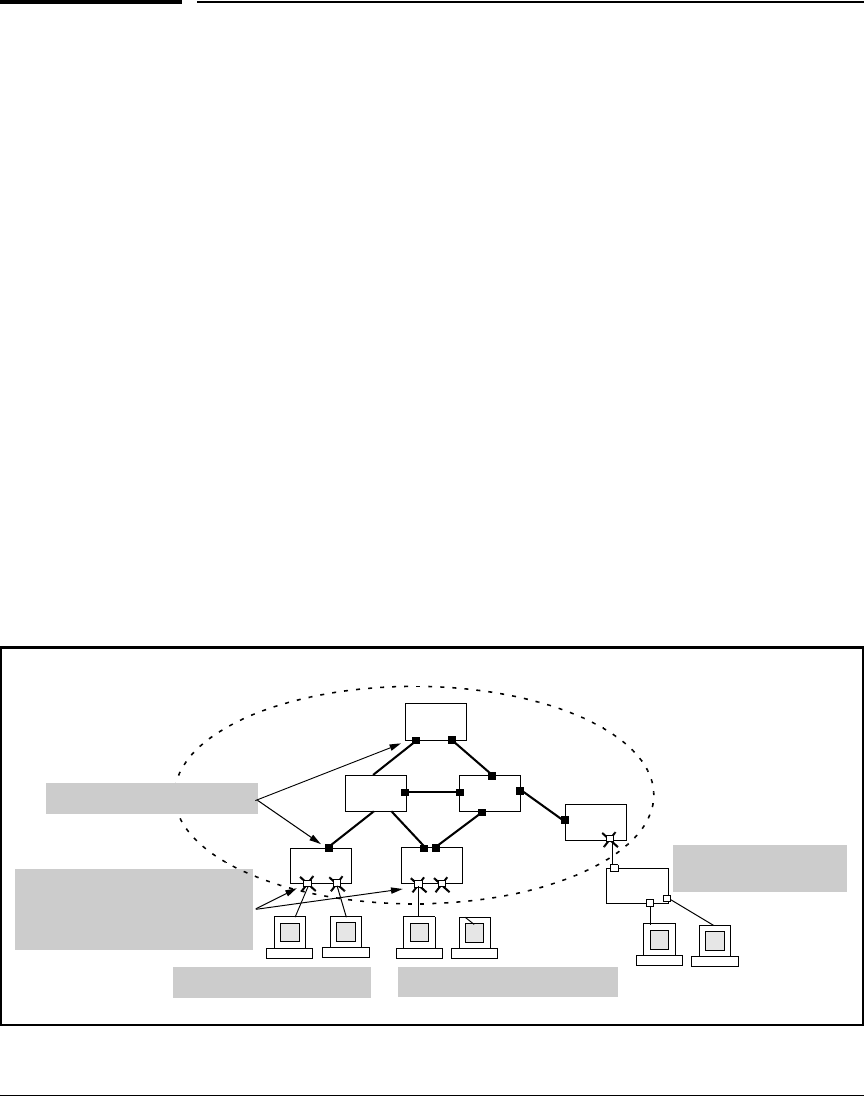
Figure 4-34 shows examples where loop protection can be used.
Unmanaged switch
(does not support STP)
Loop protection enabled ‘edge’
ports that connect to unmanaged
switches and/or authenticated
clients
Switch
STP Domain
Spanning tree enabled ports
Web authentication clients
802.1X authentication clients
Figure 4-34. Examples of Loop Protection Enabled in Preference to STP
4-74


















