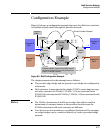
QinQ (Provider Bridging)
Introduction
• In QinQ mixed vlan mode, only ports that are members of S-VLANs
can be configured as customer network or provider network ports;
ports that are members of C-VLANs cannot be configured to any
port-type.
• QinQ mixed vlan mode devices cannot be connected in an S-VLAN
mesh topology. This is because STP cannot be run in the S-VLAN
space, and so a mesh topology (or the presence of any redundant
links) would result in loops.
• A port can only either be a member of S-VLANs or C-VLANs, but not
a combination of both.
• A port cannot be configured as a ‘Customer-Edge’ as specified in
Section 12.13.3 of the IEEE 802.1ad specification. In the current
software release, such ‘C-tagged interfaces’ are not supported—only
port-based/S-tagged interfaces are supported.
• Moving ports between C-VLANs and S-VLANs may cause conflicts.
For example, if a port has any mirroring/monitoring sessions set up,
they will not be allowed to change VLAN domains until these sessions
are unconfigured. Refer to “Changing VLAN Port Memberships
(Mixed Vlan Mode)” on page 8-22 for additional details.
■ Interoperating with Other Vendor Devices. When enabling QinQ, you
can configure a unique tpid value, such as 0x8100, to allow the device to
interoperate with devices that require this value for the inner and outer
VLAN-tag. If the provider tag-type is configured as 0x8100, then:
• customer-network ports cannot be configured as tagged-SVLAN
members; and
• tagged-SVLAN members cannot be configured as customer-network
ports.
■ Configuring QinQ with Other Network Protocols. The networks for
both the customer and provider can be complex. For information on how
QinQ may impact other network protocols (such as spanning tree, LLDP,
and GVRP), refer to “Effects of QinQ on Other Switch Features” on page
8-28.
8-12