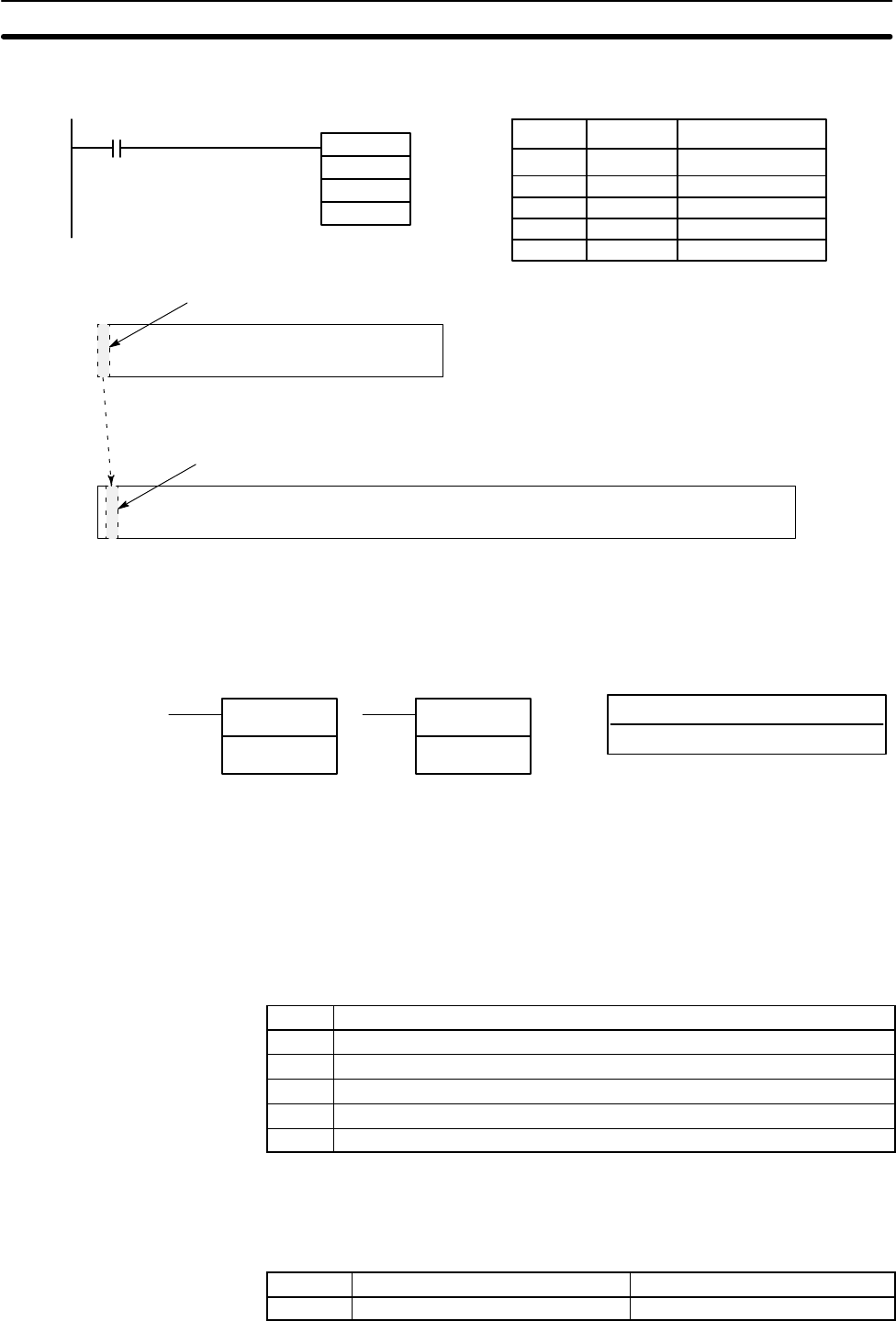
316
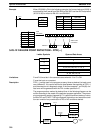
Example In the following example, the 100 word range from DM 7000 through DM 7099 is
copied to DM 0010 through DM 0109 when IR 00001 is ON.
@XDMR(––)
#7000
#0100
00001
DM 0010
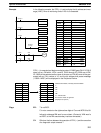
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00001
00001 @XDMR(––)
# 0100
# 7000
DM 0010
DM 7000 DM 9999
DM 7000 to DM 7099
DM 0000 DM 6143
DM 0010 to DM 0109
5-25-15 INDIRECT EM ADDRESSING – IEMS(––)
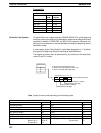
@IEMS(––)
C
C: Control word
000, #E000, or #E0B1 to #E0B3
Ladder Symbols Operand Data Areas
IEMS(––)
C
Limitations C must be 000, #E000, #E0B0, #E0B1, or #E0B2.
Description When executed with an ON execution condition, IEMS(––) changes the destina-
tion of indirect DM addressing (DM) to DM or the specified EM bank. The cur-
rent EM bank number can also be changed when indirect addressing is changed
to EM.
The destination for DM is switched to the DM area at the start of an interrupt
subroutine. It is also returned to the DM area at the beginning of each scan.
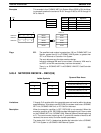
The following table shows the allowed values for C and their functions:
C IEMS(––) Operation
000 Switches the destination of DM to the DM area.
#E000 Switches the destination of DM to the current bank in the EM area.
#E0B0 Switches the destination of DM to the bank 0 in the EM area.
#E0B1 Switches the destination of DM to the bank 1 in the EM area.
#E0B2 Switches the destination of DM to the bank 2 in the EM area.
The content of DM 6031 indicates the current DM destination and the current
EM bank number as shown in the following table. Use DM 6031 in the ladder-dia-
gram program to determine if the contents of indirect DM addressing is the DM or
EM area. (Programming Devices cannot be used here because bits 08 to 15 will
always indicate the DM area when read from the Programming Device.)
Word Bits 00 to 07 Bits 08 to 15
DM 6031 Current EM bank number (00 to 02) DM destination (00: DM; 80: EM)
Special Instructions Section 5-25