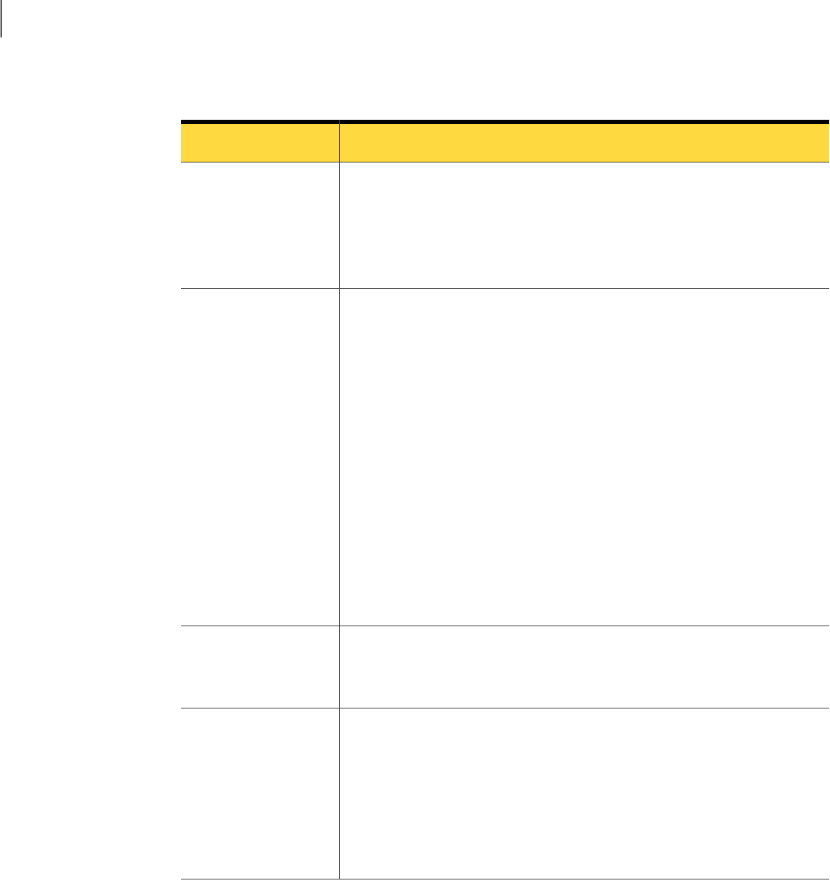
Table 8-4
LLT directives
DescriptionDirective
Assigns the system ID or symbolic name. The system ID number
must be unique for each system in the cluster, and must be in the
range0-31. Thesymbolicname correspondstothesystem IDinthe
/etc/llthostsfile.Note thatLLT failsto operateifany systemsshare
the same ID.
set-node
Attaches LLT to a network interface. At least one link is required,
and up to eight are supported. The first argument to link is a
user-definedtag shownin thelltstat(1M) outputto identifythe
link. It may also be used in llttab to set optional static MAC
addresses.
The second argument to link is the device name of the network
interface. Its format is device_name:device_instance_number. The
remaining four arguments to link are defaults; these arguments
should be modified only in advanced configurations. There should
be one link directive for each network interface. LLT uses an
unregistered Ethernet SAP of 0xCAFE. If the SAP is unacceptable,
refer to the llttab(4) manual page for information on how to
customize SAP. Note that IP addresses do not need to be assigned
to the network device; LLT does not use IP addresses.
link
Assignsauniqueclusternumber.Usethisdirectivewhenmorethan
oneclusteris configuredonthesame physicalnetworkconnection.
LLT uses a default cluster number of zero.
set-cluster
Use this directive in place of link for public network interfaces.
This directive prevents VCScommunication on the public network
until the network is the last link, and reduces the rate of heartbeat
broadcasts.Note thatLLT distributesnetwork trafficevenly across
all available network connections. It also enables VCS
communication,andbroadcastsheartbeatstomonitoreach network
connection.
link-lowpri
For more information about LLT directives, refer to the llttab(4) manual page.
Additional considerations for LLT
You must attach each network interface that is configured for LLT to a separate
and distinct physical network.
Installing VCS on a single node
Adding a node to a single-node cluster
148


















