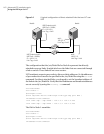
■ See “Sample configuration: direct-attached links” on page 161.
■ See “Sample configuration: links crossing IP routers” on page 163.
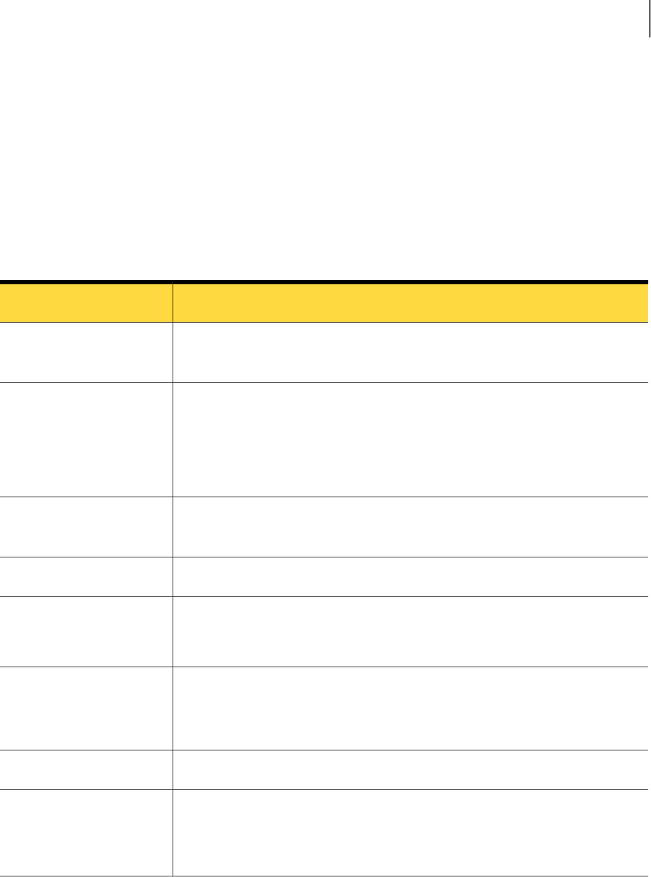
TableA-1 describesthe fieldsof thelink commandthat areshown inthe /etc/llttab
file examples.Note that some of the fields differ from the commandfor standard
LLT links.
Table A-1
Field description for link command in /etc/llttab
DescriptionField
A unique string that is used as a tag by LLT; for example link1,
link2,....
tag-name
The device path of the UDP protocol; for example udp.
A placeholder string. On otherunix platforms likeSolaris or HP,
this entry points to a device file (for example, /dev/udp). Linux
does not have devices for protocols. So this field is ignored.
device
Nodes using the link. "-" indicates all cluster nodes are to be
configured for this link.
node-range
Type of link; must be "udp" for LLT over UDP.link-type
Unique UDP port in the range of 49152-65535 for the link.
See “Selecting UDP ports” on page 160.
udp-port
"-" is the default, which has a value of 8192. The value may be
increased or decreased depending on the configuration. Use the
lltstat -l command to display the current value.
MTU
IP address of the link on the local node.IP address
■ For clusters with enabled broadcasts, specify the value of the
subnet broadcast address.
■ "-" is the default for clusters spanning routers.
bcast-address
The set-addr command in the /etc/llttab file
The set-addr command in the /etc/llttab file is required when the broadcast
feature of LLT is disabled, such as when LLT must cross IP routers.
See “Sample configuration: links crossing IP routers” on page 163.
Table A-2 describes the fields of the set-addr command.
159Advanced VCS installation topics
Using the UDP layer for LLT