3Com Switch 8800 Configuration Guide Chapter 33 QoS Configuration
33-4
Packets sent via this
interface
high priority
Low priority
Classify
Packets sent
Sending queueDequeue
queue 7
queue 6
queue 5
queue 4
queue 3
queue 2
queue 1
queue 0
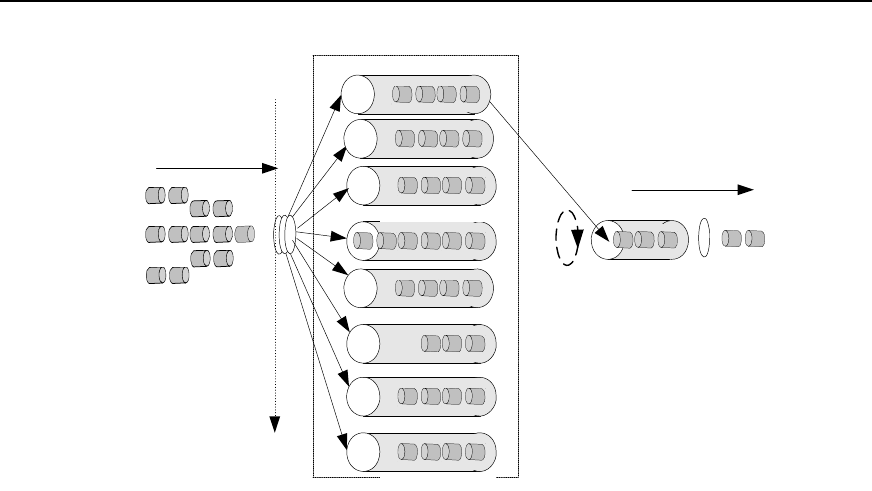
Figure 33-4 Priority queues
SP algorithm is designed for key services. One of the characteristics of key services is
these services should be processed first to minimize response delay during switch
congestion. For example, there are eight outbound queues at the port, numbered
respectively as 7 to 0, with priority levels in descending order.
In SP mode, the system first sends those packets of higher priority in strict accordance
with priority order. Only when packets in high priority queue are all sent can those in
lower priority queue be sent. This manner of putting key-service packets into high
priority queue and non-key service packets into low priority queue does ensure that
key-service packets are sent first, while non-key service packets are sent during the
interval when no key-service packets needs to be processed.
SP algorithm also has its disadvantages: If high priority queues always have packets for
a long period, then the packets in low queues may die of hunger for being processed.
2) WRR algorithm
Each port supports eight outbound queues except that port of XP4 board only supports
four queues. In WRR mode, the system processes the queues by turn, so every queue
can have a service period.
See the case where the port supports eight outbound queues. Every queue is assigned
with a weight value (respectively numbered as w7, w6, w5, w4, w3, w2, w1 and w0),
which indicates the weight in obtaining resources. For a 100 Mbps port, the weight
values are set as 50, 30, 10, 10, 50, 30, 10 and 10 (corresponding respectively to w7,
w6, w5, w4, w3, w2, w1 and w0). The even the queue with the lowest priority can be
allocated with a 5 Mbps bandwidth.


















