20050401
3-2-3
Manipulating List Data
Example To create a 2-row × 3-column matrix (each cell of which
contains 0) in Matrix A
A!*(
{ )c,d!/( } )a
K1(LIST)3(Dim)
K2(MAT)1(Mat)av(A)w
The following shows the new contents of Mat A.
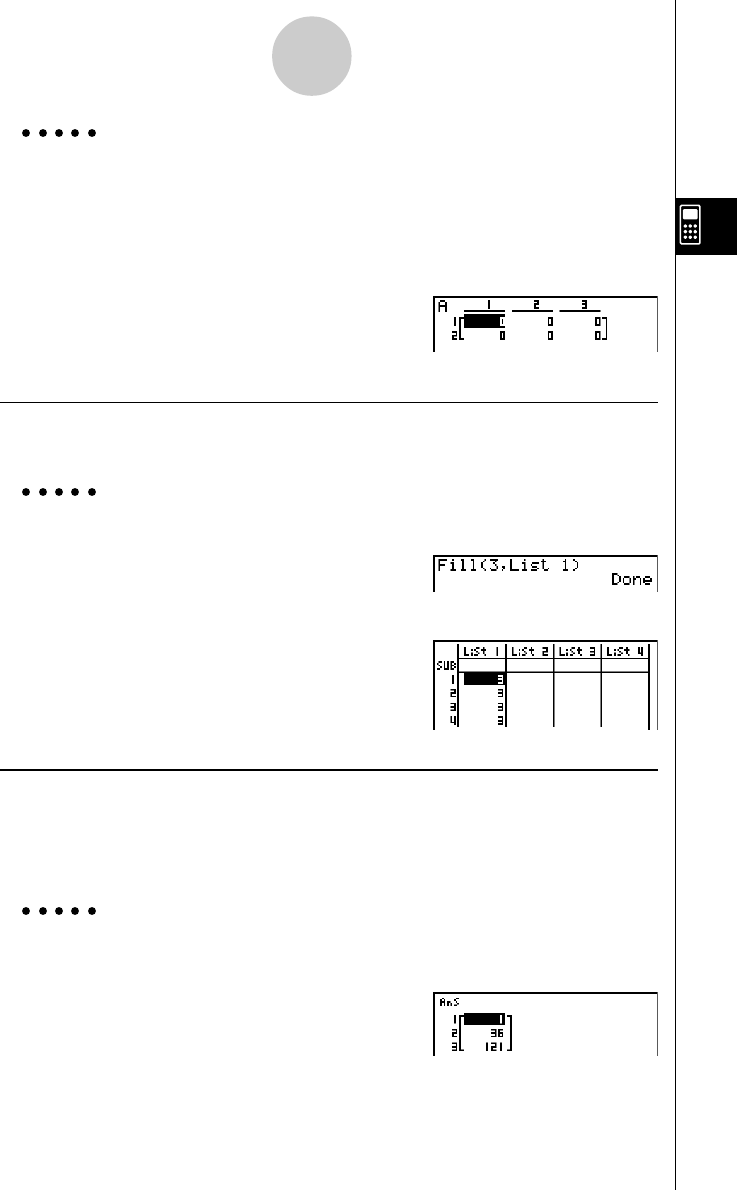
u To replace all data items with the same value [OPTN]-[LIST]-[Fill]
K1(LIST)4(Fill) <value>,1(List) <list number 1-26>)w
Example To replace all data items in List 1 with the number 3
AK1(LIST)4(Fill)
d,1(List)b)w
The following shows the new contents of List 1.
u To generate a sequence of numbers [OPTN]-[LIST]-[Seq]
K1(LIST)5(Seq) <expression> , <variable name> , <start value>
, <end value> , <increment> ) w
• The result of this operation is stored in ListAns Memory.
Example To input the number sequence 1
2
, 6
2
, 11
2
, into a list, using the function
f(x) = X
2
. Use a starting value of 1, an ending value of 11, and an
increment of 5
AK1(LIST)5(Seq)vx,
v,b,bb,f)w
Specifying an ending value of 12, 13, 14, or 15 produces the same result as shown above,
because all of them are less than the value produced by the next increment (16).


















