9-1
CHAPTER
9
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
Replacement
This chapter explains the replacement procedures for the power supply unit (PSU).
It covers the following:
■ Section 9.1, “Overview of the PSU” on page 9-1
■ Section 9.2, “Active Replacement and Hot Replacement” on page 9-8
■ Section 9.3, “Cold Replacement” on page 9-12
There are three methods for replacing a PSU: active replacement , hot replacement,
and cold replacement. For the definition of each type of method, see Section 4.1,
“Types of Replacement Procedures” on page 4-2.
The same power supply unit is mounted on the rack-mountable dual power feed
option or power cabinet (see Chapter 24). The orientation of the mounted power
supply unit may vary by 90 degrees, but the replacement procedure is the same. See
the procedure described in subsequent sections.
9.1 Overview of the PSU
This section provides an overview of the PSU and describes its mounting locations.
A PSU receives alternating power, and it distributes 48 V and 12 V of direct current
to each component. PSUs have an N+1 redundancy configuration, and active
maintenance can be performed on them.
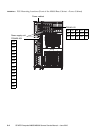
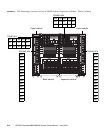
FIGURE 9-1 and FIGURE 9-2 show the PSU locations inside the M8000 server. FIGURE 9-3
and
FIGURE 9-4 show the PSU locations inside the M9000 server (base cabinet).
FIGURE 9-5 and FIGURE 9-6 show the PSU locations inside the M9000 server (with an
expansion cabinet).