Troubleshooting
DNS Resolver
Syntax: [no] ip dns domain-name < domain-name-suffix >
This optional DNS command configures the domain suffix that is automatically
appended to the host name entered with a DNS-compatible command. When the
domain suffix and the IP address for a DNS server that can access that domain are
both configured on the switch, you can execute a DNS-compatible command using
only the host name of the desired target. (For an example, refer to Figure C-35 on
page C-88.) In either of the following two instances, you must manually provide the
domain identification by using a fully qualified DNS name with a DNS-compatible
command:
• If the DNS server IP address is configured on the switch, but the domain suffix
is not configured (null)
• The domain suffix configured on the switch is not the domain in which the target
host exists
The switch supports one domain suffix entry and three DNS server IP address
entries. (Refer to the preceding command description.)
The no form of the command replaces the configured domain suffix with the null
setting. (Default: null)
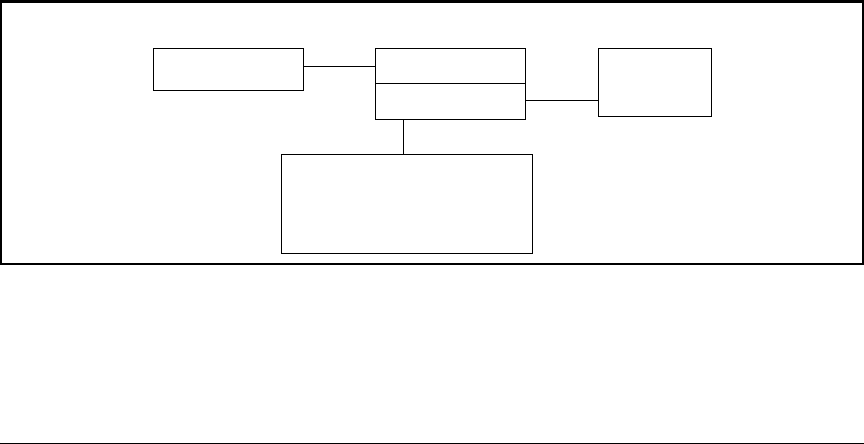
Example Using DNS Names with Ping and Traceroute
In the network illustrated in Figure C-37, the switch at 10.28.192.1 is config-
ured to use DNS names for DNS-compatible commands in the
pubs.outdoors.com domain. The DNS server has been configured to assign the
host name docservr to the IP address used by the document server
(10.28.229.219).
Switch “A” Configured
Document
with DNS Resolver
Router “B”
Server
docservr
10.28.192.2
10.28.192.1
(10.28.229.219)
10.28.229.1
DNS Server for pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.229.10
Host Name for IP address
Domain: pubs.outdoors.com
10.28.229.219 = “docservr”
Figure C-37. Example Network Domain
C-91


















