OCPRF100 MP Server System Technical Product Specification
Revision 1.0
114
All of the front panel’s functions are controlled by a Philips 80C652 microcontroller and are avail-
able at all times when AC power is available. The connection from the front panel to the rest of
the OCPRF100 MP server system is via the 80-pin connector to the OCPRF100 Profusion car-
rier. All six system fans plug into the OCPRF100 MP server system front panel. Circuitry located
on the front panel controls the fan speed, monitors individual fan tachometer signals, and indi-
cates (via LEDs) the failure of an individual fan in the system.
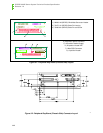
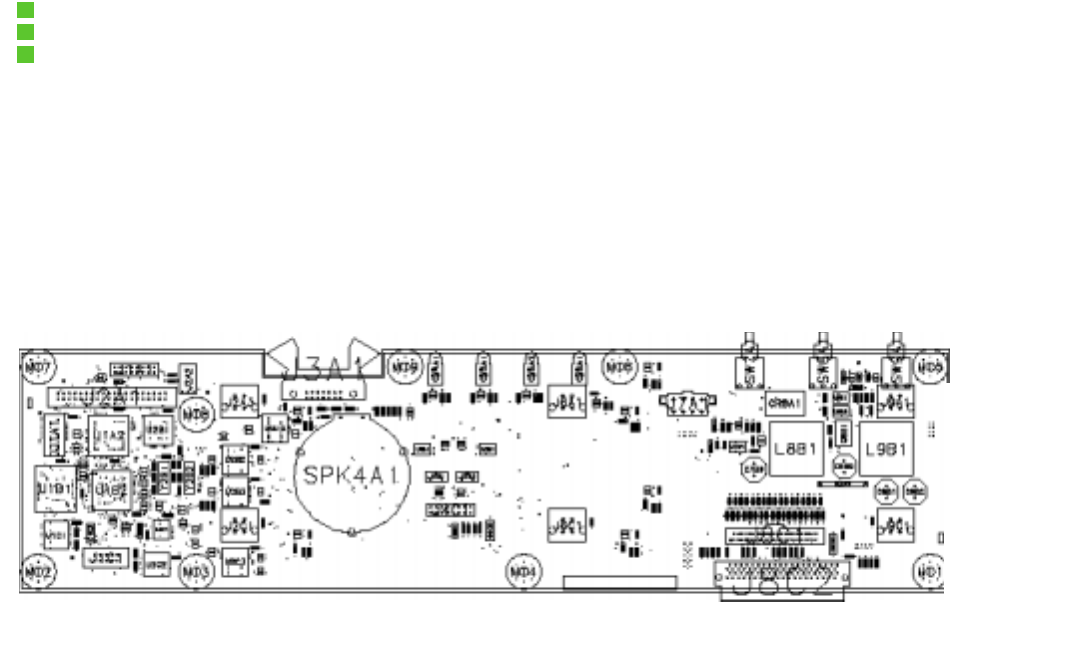
Figure 10-1: OCPRF100 MP Server System Front Panel Layout
10.2 Functional Description
This section provides a functional description of the front panel including the microcontroller,
push buttons, indicator LEDs, LCD panel, ICMB, and RS-232 extension.
10.2.1 Microcontroller
All of the “intelligent” functions on the front panel are implemented with a Philips 80C652 micro-
controller (also referred to in this document as the FPC). The FPC has 32KB of RAM, 7.5KB of
which is accessible; and, 64KB of flash, 56KB of which is accessible. The flash contains all of the
firmware the front panel needs, while the RAM is used to store the stack and local variables.
The microcontroller is always active as long as AC power is present. This power is also known as
5 V standby power, standby power, or always-alive power. The microcontroller records the cur-
rent power state (on or off) in its nonvolatile memory (NVM); in the event of an AC power failure,
the FPC can return the system’s power status to the state it was in prior to the power failure.
The microcontroller constantly monitors the switches, the state of the power supplies (via its pri-
vate I
2
C bus, I2C_FPC_Sxx), and the ICMB, which is described below in further detail. While the
system is powered on, the front panel also monitors the IPMB and responds to IPMB messages.
10.2.2 Memory Maps
This section contains a device maps subsection and an I/O memory maps subsection.