Chapter 7: Programming 7-35
2.
None -- Scan the Hex 2 tag to select none. No label identifiers are
added to the message data.
3.
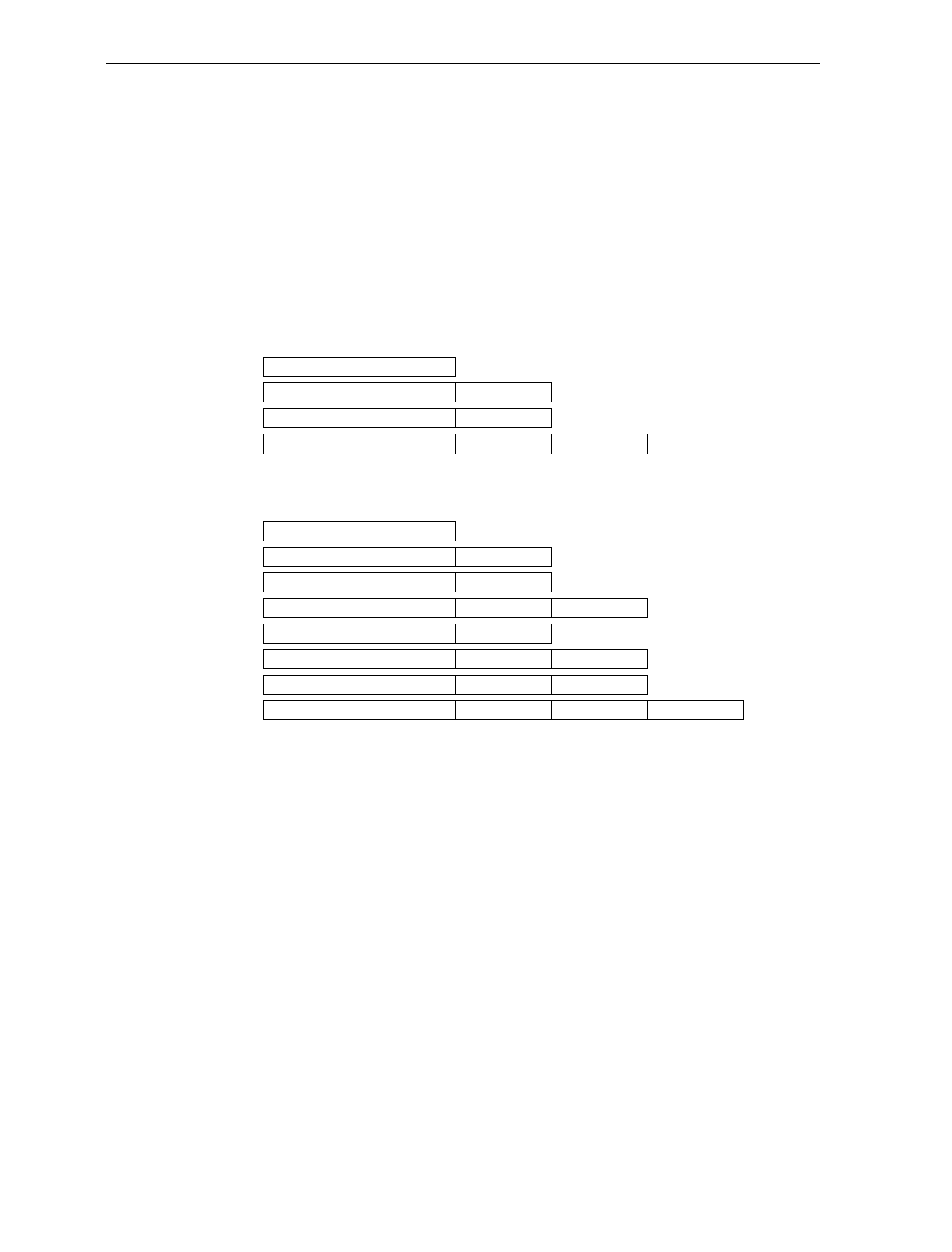
Unique Prefix – - To use a unique prefix, scan the Hex 3. A Unique
Identifier is associated with each bar code type. Also, you may use
one, two, or no Common Bytes. The figure shows the possible
message formats when using a unique prefix. The formats do not
show other elements programmed in the other RS-232
programming modes.
Unique Prefix - All Bar Codes
Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 1 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 1 Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Unique Prefix - UPC Version D
Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 1 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Common Byte 1 Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code Data
Unique Identifier Bar Code DataVersion Number
Common Byte 1 Unique Identifier Bar Code DataVersion Number
Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code DataVersion Number
Common Byte 1 Common Byte 2 Unique Identifier Bar Code DataVersion Number
R0147
Common Byte 1 and Common Byte 2
The Common Byte 1 and Common Byte 2 parameters permit you to
specify the data sent to the host terminal in the Common Byte fields.
Enter this information as two Hex characters for each Common Byte.


















