Using the BayStack 450 10/100/1000 Series Switch
1-72
302401-D Rev 00
Spanning Tree Considerations for MultiLink Trunks
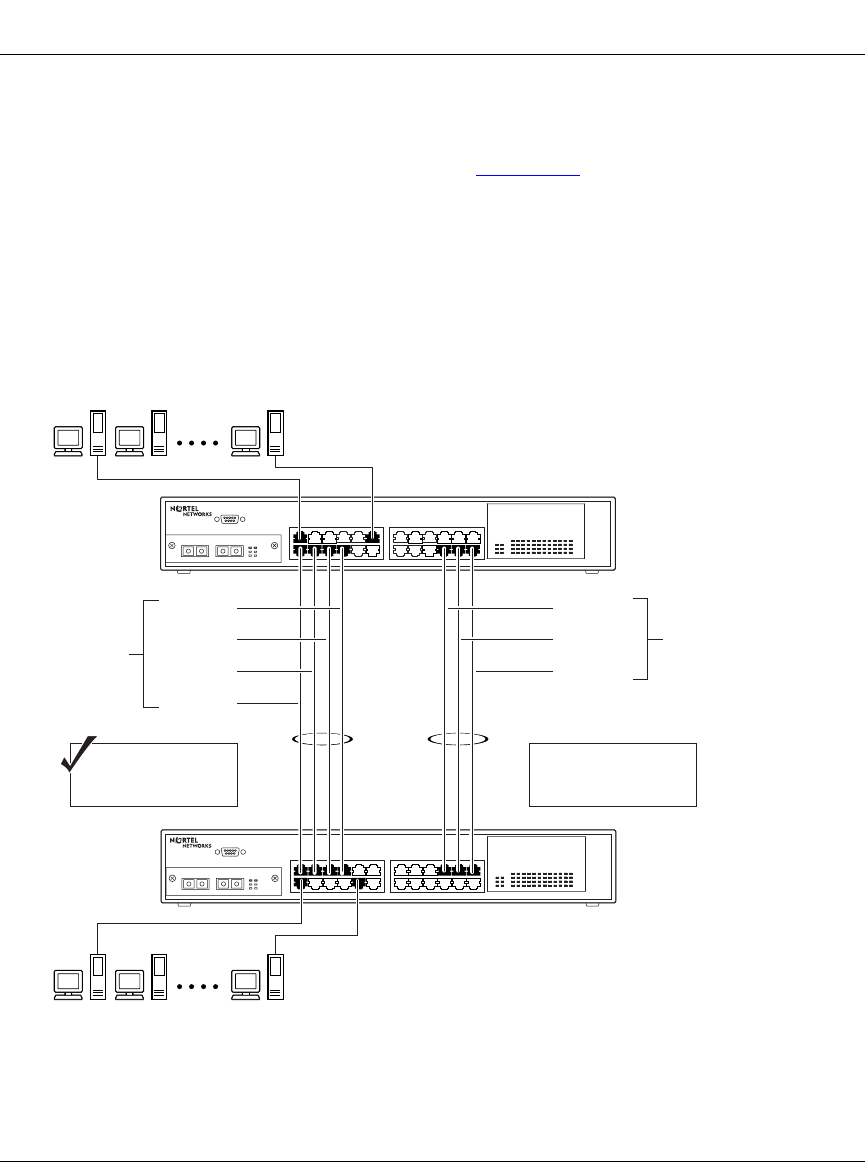
The spanning tree Path Cost parameter is recalculated based on the aggregate
bandwidth of the trunk. For example, Figure 1-47
shows a four-port trunk (T1)
with two port members operating at 100 Mb/s and two at 10 Mb/s. Trunk T1
provides an aggregate bandwidth of 220 Mb/s. The Path Cost for T1 is 4 (Path
Cost = 1000/LAN speed, in Mb/s). Another three-port trunk (T2) is configured
with an aggregate bandwidth of 210 Mb/s, with a comparable Path Cost of 4.
When the Path Cost calculations for both trunks are equal, the software chooses
the trunk with the larger aggregate bandwidth (T1) to determine the most efficient
path.
Figure 1-47. Path Cost Arbitration Example
BS45029A
T1 T2
100 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
100 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
10 Mb/s
Path Cost T1 = 4
S1
S2
Path Cost T2 = 4
Aggregate Bandwidth
220 Mb/s
Aggregate Bandwidth
210 Mb/s
kombk.book Page 72 Tuesday, June 29, 1999 3:25 PM


















