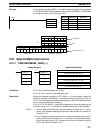
Y
0
X
0
X
1
X
2
X
3
X
4
X
m
X
Y
Y
m
Y
4
Y
3
Y
1
Y
2
265
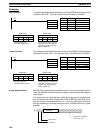
Enter the coordinates of the m+1 end-points, which define the m line segments,
as shown in the following table. Enter all coordinates in BIN form. Always enter
the coordinates from the lowest X value (X
1
) to the highest (X
m
). X
0
is 0000, and
does not have to be entered.
Word Coordinate
C+1 X
m
(max. X value)
C+2 Y
0
C+3 X
1
C+4 Y
1
C+5 X
2
C+6 Y
2
↓ ↓
C+(2m+1) X
m
C+(2m+2) Y
m
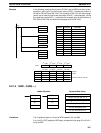
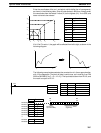
If bit 13 of C is set to 1, the graph will be reflected from left to right, as shown in the
following diagram.
X
0
X
m
X
Y
X
m
X
0
X
Y
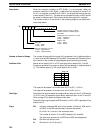
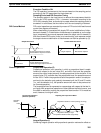
The following example demonstrates the construction of a linear approximation
with 12 line segments. The block of data is continuous, as it must be, from DM
0000 to DM 0026 (C to C + (2 × 12 + 2)). The input data is taken from IR 010, and
the result is output to IR 011.
DM 0000 $C00B
DM 0001 $05F0 X
12
DM 0002 $0000 Y
0
DM 0003 $0005 X
1
DM 0004 $0F00 Y
1
DM 0005 $001A X
2
DM 0006 $0402 Y
2
↓↓↓
DM 0025 $05F0 X
12
DM 0026 $1F20 Y
12
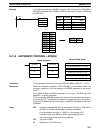
APR(69)
DM 0000
010
011
00000
1 1 0 0 000000001011
Bit
15
Bit
00
(Output and
input both BIN)
(m–1 = 11: 12 line
segments)
Content Coordinate
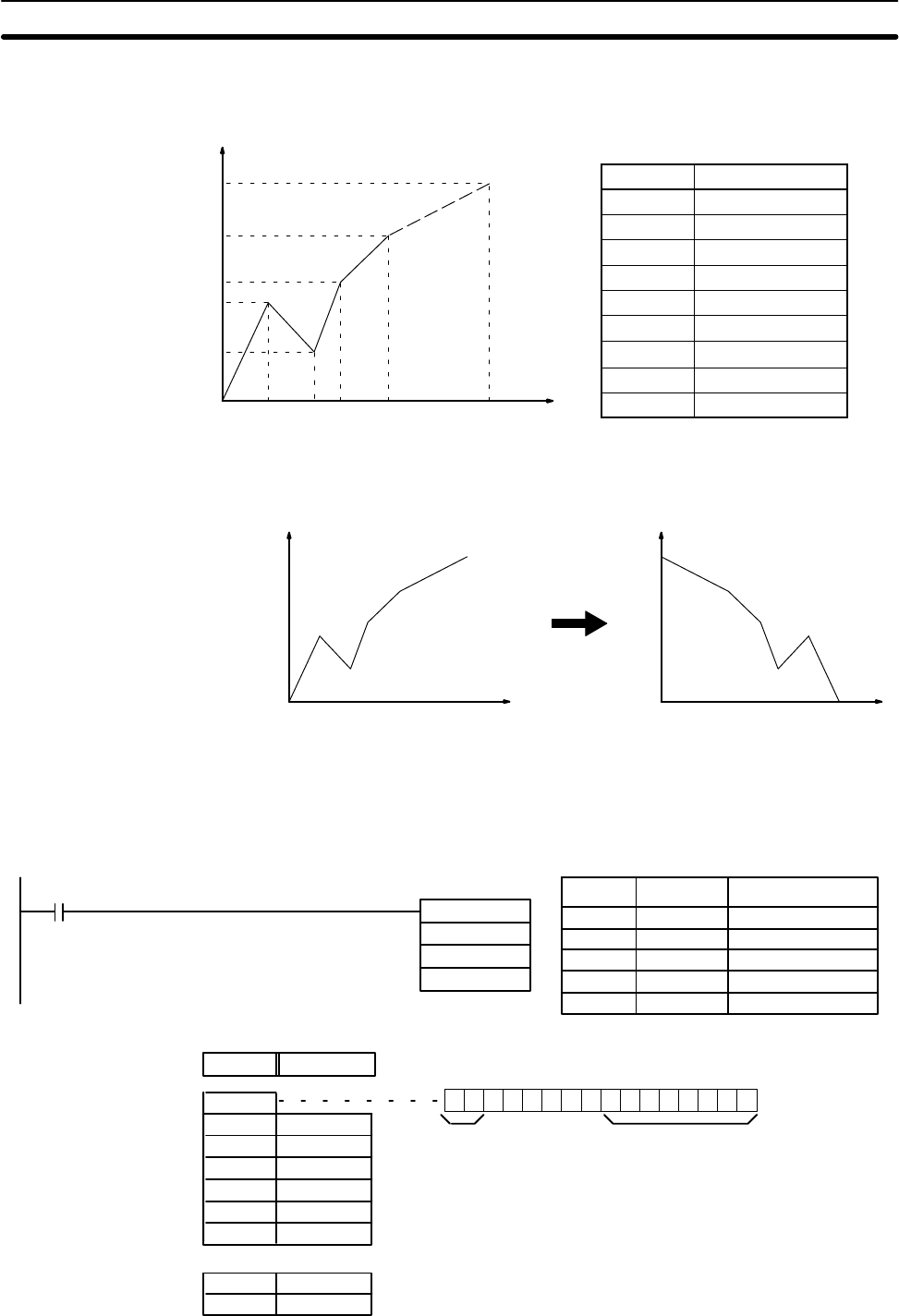
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 APR(69)
DM 0000
010
011
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21