271
PID Operation
PID operation combines proportional operation (P), integral operation (I), and
derivative operation (D). It produces superior control results even for control ob-
jects with dead time. It employs proportional operation to provide smooth control
without hunting, integral operation to automatically correct any offset, and deriv-
ative operation to speed up the response to disturbances.
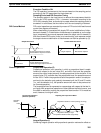
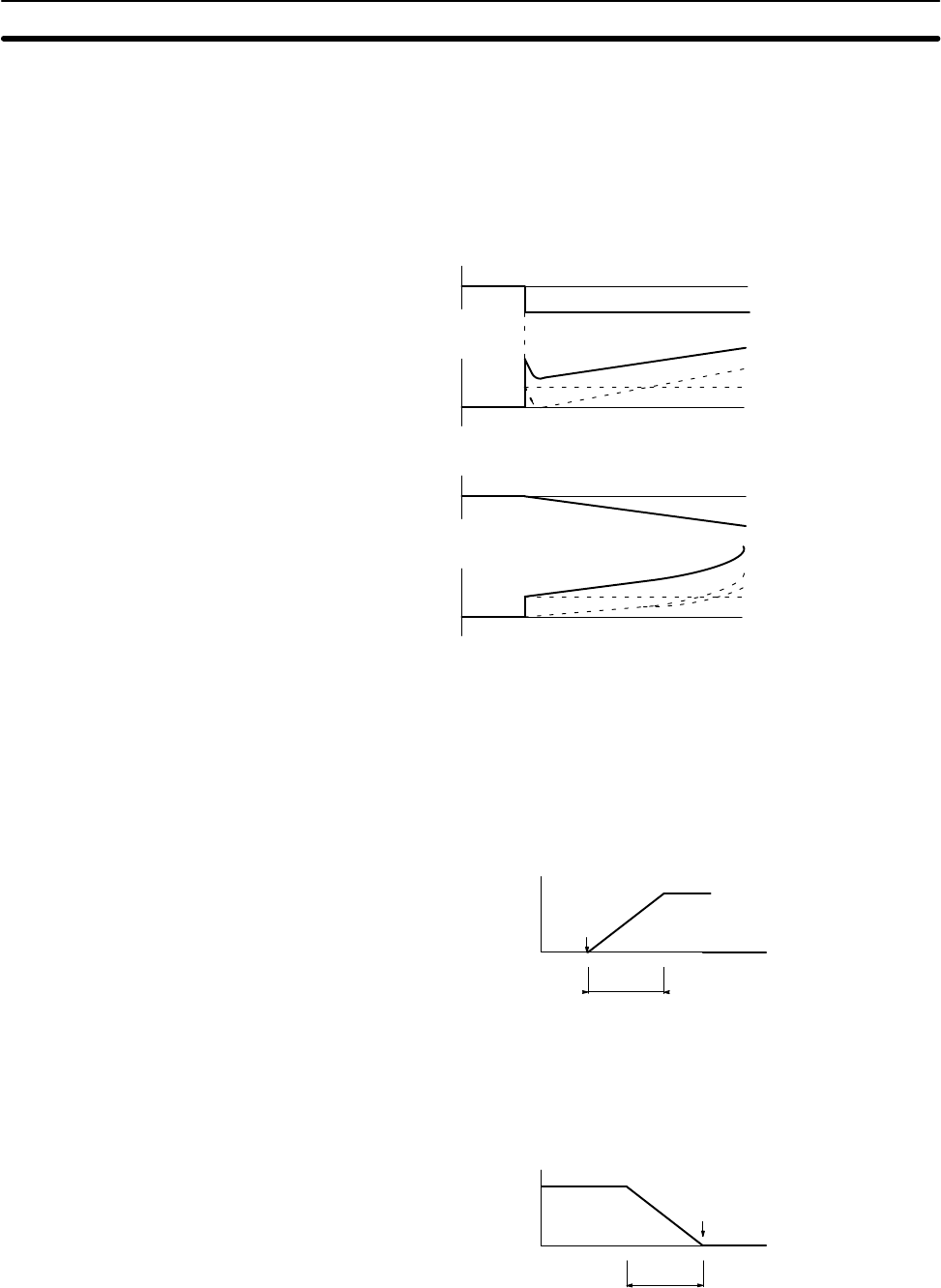
PID Operation Output Step Response
PID Operation Output Ramp Response
PID operation
I operation
P operation
D operation
Step response
0
0
Deviation
Operation
amount
PID operation
I operation
P operation
D operation
Ramp response
0
0
Deviation
Operation
amount
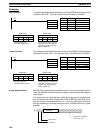
Direction of Operation When using PID operation, select either of the following two control directions. In
either direction, the operation amount increases as the difference between the
SV and the PV increases.
• Forward operation: Control amount is increased when the SV is larger than the
PV.
Forward Operation
Operation
amount
SV
Proportional band
100%
0%
Low High
• Reverse operation: Control amount is decreased when the SV is smaller than
the PV.
Reverse Operation
Operation
amount
SV
Proportional band
100%
0%
Low High
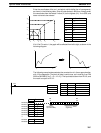
Adjusting PID Parameters The general relationship between PID parameters and control status is shown
below.
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21