350
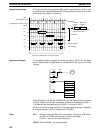
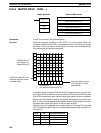
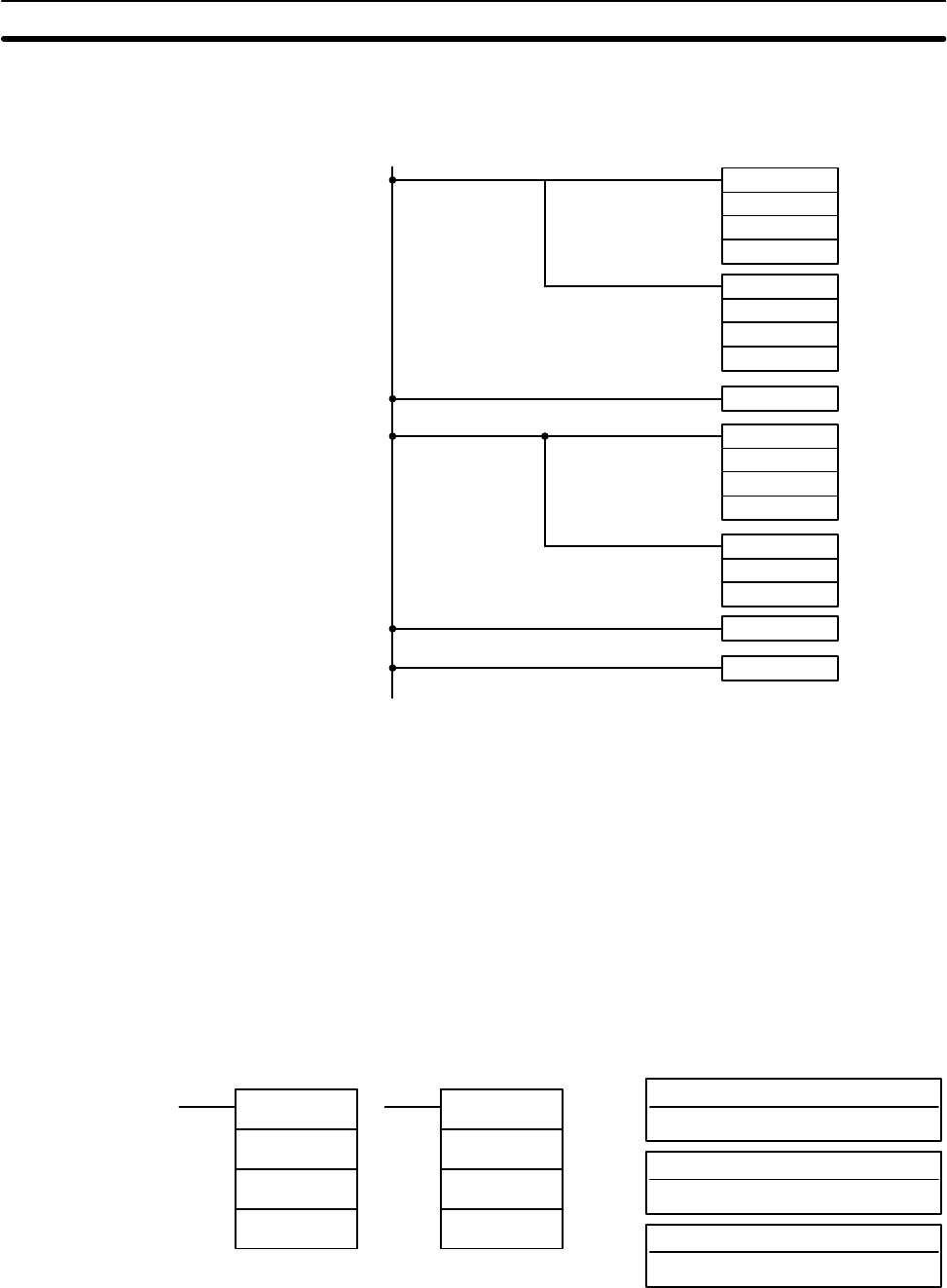
Example The following examples shows programming MTR(––) in a scheduled subrou-
tine, where IORF(97) is programmed to ensure that the I/O words used by
MTR(––) are refreshed each time MTR(––) is executed.
INT(89)
001
004
# 0002
INT(89)
000
004
# 0002
SBN(92) 99
MTR(––)
S
D1
D2
IORF(97)
D1
D2
RET(93)
END(01)
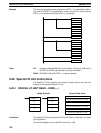
Flags ER: Indirectly addressed DM word is non-existent. (Content of DM word is
not BCD, or the DM area boundary has been exceeded.)
25403: SR 25403 is ON while MTR(––) is being executed.
5-29 Special I/O Unit Instructions
The Special I/O Unit instructions are used to transfer data to and from the
memory of the specified Special I/O Unit.
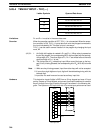
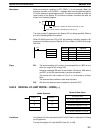
5-29-1 SPECIAL I/O UNIT READ – IORD(––)
C: Control code
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
S: Source information
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Operand Data Areas
D: First destination word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR
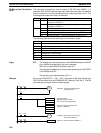
Ladder Symbols
IORD(––)
C
S
D
@IORD(––)
C
S
D
Limitations Only Special I/O Units mounted to the PC’s CPU Rack or Expansion I/O Racks
can be specified.
The last three digits of S must be BCD (from 001 to 128).
Special I/O Unit Instructions Section 5-29