384
The minimum and maximum I/O response times are shown here, using as an
example the following instructions executed at the master and the slave. In this
example, communications proceed from the master to the slave.
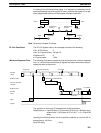
Input
Output (LR) Input
(LR)
Output
The following conditions are taken as examples for calculating the I/O response
times.
Input ON delay: 8 ms
Master cycle time: 10 ms
Slave cycle time: 14 ms
Output ON delay: 10 ms
Number of LR words: 64 words
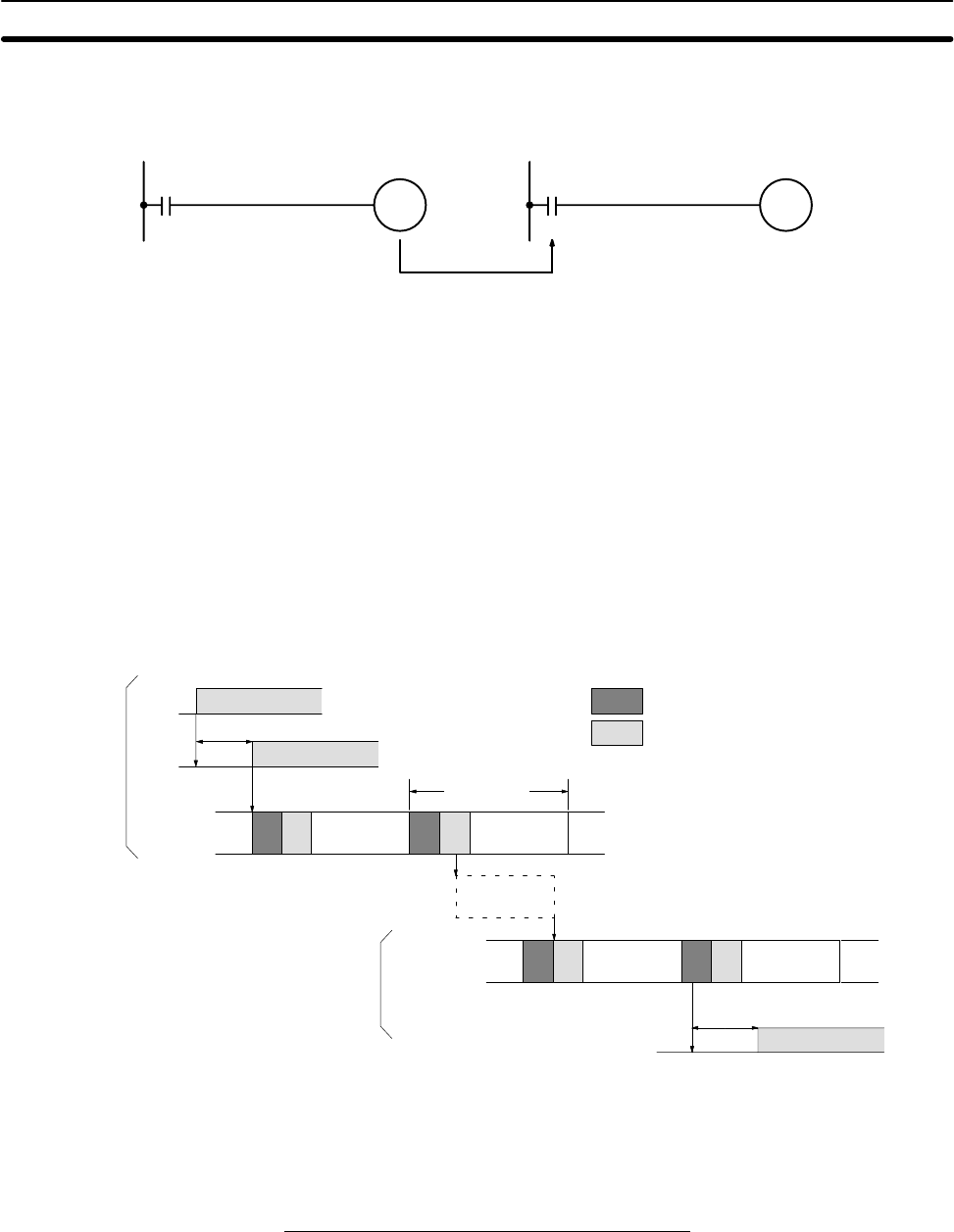
Minimum I/O Response Time The C200HX/HG/HE responds most quickly under the following circumstances:
1, 2, 3... 1. The C200HX/HG/HE receives an input signal just prior to the input refresh
phase of the cycle.
2. The master to slave transmission begins immediately.
3. The slave executes communications servicing immediately after comple-
tion of communications.
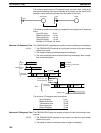
Master
Input
point
Input
bit
CPU Unit
processing
I/O refresh
Overseeing, communica-
tions, etc.
Cycle time
Input ON delay
One-to-one link
communications
Master to
Slave
CPU Unit
processing
Slave
Instruction
execution
Instruction
execution
Instruction
execution
Instruction
execution
Output point
Output ON
delay
The minimum I/O response time is as follows:
Input ON delay: 8 ms
Master cycle time: 10 ms
Transmission time: 39 ms
Slave cycle time: 15 ms
+ Output ON delay: 10 ms
Minimum I/O response time: 82 ms
Maximum I/O Response Time The C200HX/HG/HE takes the longest to respond under the following circum-
stances:
1, 2, 3... 1. The C200HX/HG/HE receives an input signal just after the input refresh
phase of the cycle.
2. The master to slave transmission does not begin immediately.
I/O Response Time Section 6-4