Chapter 1 Overview of the TimeProvider
Synchronization Status Messages (SSMs)
42 TimeProvider User’s Guide 097-58001-02 Revision G – April 2008
The TimeProvider handles SSMs in accordance with T1X1.3 TR33, T1.101-1999,
GR-253, and GR-378.
Input SSMs
The TimeProvider extracts and decodes the SSM (if present) on the available
inputs. Using this information, the TimeProvider can automatically select the input
with the higher quality level.
You can manually provision the input quality level for those signals that do not have
SSM information or you can provision INP1 and INP2 to read the SSM on the input;
in either case the quality level of the reference input becomes the system’s quality
level, which is passed through to the outputs in the output SSM. If the IOC enters
the Free-run or Holdover mode, the system’s quality level is determined by the
CLKTYPE parameter for the local oscillator on the selected IOC module. You can
provision the CLKTYPE parameter to Type I, Type II, ST2, or ST3E.
Output SSMs
You must provision the TimeProvider’s outputs according to the type of SSM
operation you are using:
For ANSI SSM operation, set the output type to Extended SuperFrame (ESF) for
ANSI SSM operation.
For ITU SSM operation, set the output type to Channel Associated Signaling
(CAS) or Common Channel Signaling (CCS) with CRC4 framing. The SSM bit
location can be set by the user.
SONET Minimum Clock traceable
(20 ppm clock)
7SMC
Stratum 4 traceable (32 ppm clock) 8 ST4
Do Not Use for synchronization 9 DUS
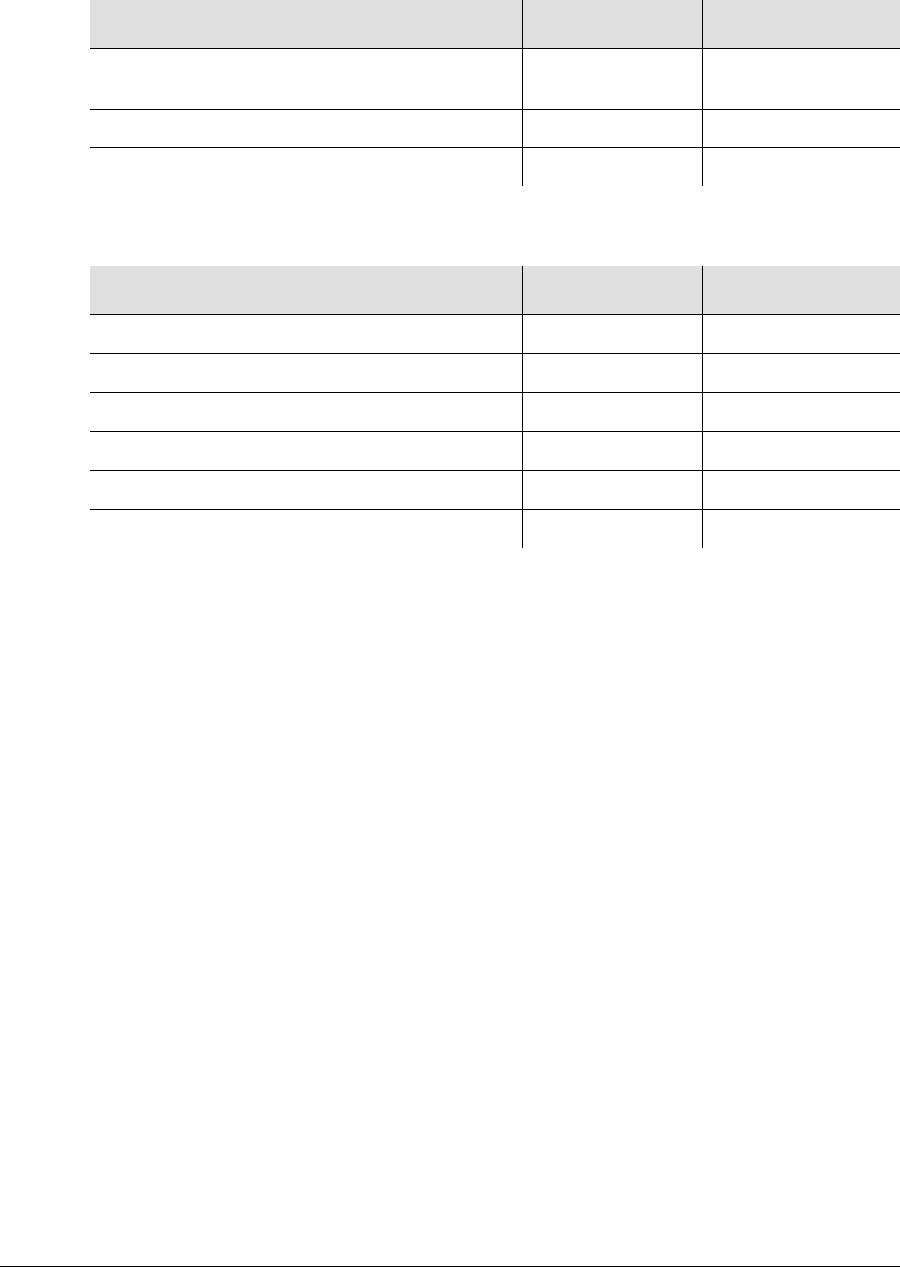
Table 1-5. ITU SSM Quality Level Definitions
Description Quality Level Abbreviation
Synchronized – Traceability Unknown 0 UNK
Primary Reference Clock 2 PRC
Transit Node 4 SSUT
Local Node 8 SSUL
Synchronization Equipment Clock 11 SEC
Do Not Use for synchronization 15 DNU
Table 1-4. ANSI SSM Quality Level Definitions (Continued)
Description Quality Level Abbreviation


















