Accessing the Flash Module
PRELIMINARY
2-5
Flash Operations and Control Registers
PRELIMINARY
2.2 Accessing the Flash Module
In addition to the flash memory array, each flash module has four registers that
control operations on the flash array. These registers are:
- Segment control register (SEG_CTR)
- Test register (TST)
- Write address register (WADRS)
- Write data register (WDATA)
The flash module operates in one of two modes: one in which the flash memory
is accessed directly by the CPU, and one in which the memory array cannot
be accessed directly, but the four control registers are accessible. This mode
is used for programming. Each flash module has a flash access-control regis-
ter that selects between these two access modes. The register is a single-bit,
I/O-mapped register.
The two access modes are summarized as follows:
- Array-access mode. You can access the flash array in the memory space
decoded for the flash module. The flash module remains in this mode most
of the time, because it allows the DSP core to read from the memory array.
- Register-access mode. You can access the four control registers in the
memory space decoded for the flash module. This mode is used for pro-
gramming. When the flash module is in register-access mode, the regis-
ters are repeated every four address locations within the flash module’s
address range.
The flash array is not directly accessible as memory in register-access mode,
and the control registers are not directly accessible in array-access mode.
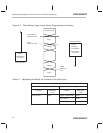
Figure 2–2 shows memory maps of the flash array in register and array access
modes.