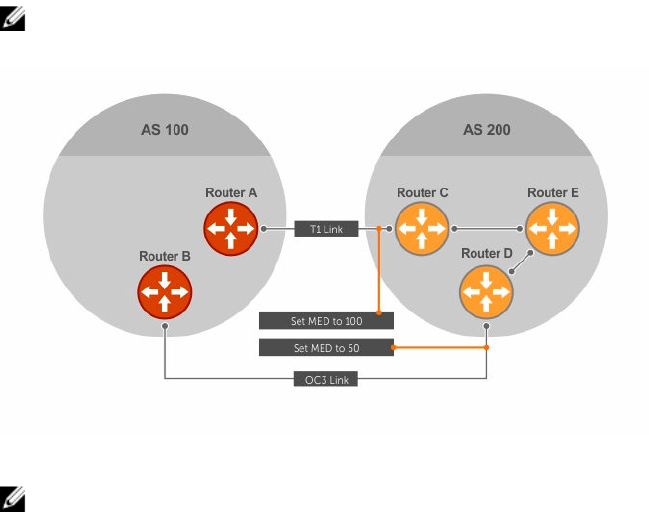
connect in two places. Each connection is a BGP session. AS200 sets the MED for its T1 exit point to 100
and the MED for its OC3 exit point to 50. This sets up a path preference through the OC3 link. The MEDs
are advertised to AS100 routers so they know which is the preferred path.
MEDs are non-transitive attributes. If AS100 sends an MED to AS200, AS200 does not pass it on to AS300
or AS400. The MED is a locally relevant attribute to the two participating ASs (AS100 and AS200).
NOTE: The MEDs are advertised across both links, so if a link goes down, AS 1 still has connectivity
to AS300 and AS400.
Figure 22. Multi-Exit Discriminators
NOTE: Configuring the set metric-type internal command in a route-map advertises the
IGP cost as MED to outbound EBGP peers when redistributing routes. The configured
set metric
value overwrites the default IGP cost. If the outbound route-map uses MED, it overwrites IGP MED.
Origin
The origin indicates the origin of the prefix, or how the prefix came into BGP. There are three origin
codes: IGP, EGP, INCOMPLETE.
Origin Type Description
IGP Indicates the prefix originated from information learned through an interior
gateway protocol.
EGP Indicates the prefix originated from information learned from an EGP protocol,
which NGP replaced.
INCOMPLETE Indicates that the prefix originated from an unknown source.
Generally, an IGP indicator means that the route was derived inside the originating AS. EGP generally
means that a route was learned from an external gateway protocol. An INCOMPLETE origin code
generally results from aggregation, redistribution, or other indirect ways of installing routes into BGP.
Border Gateway Protocol IPv4 (BGPv4)
173


















