FCoE Transit Configuration Example
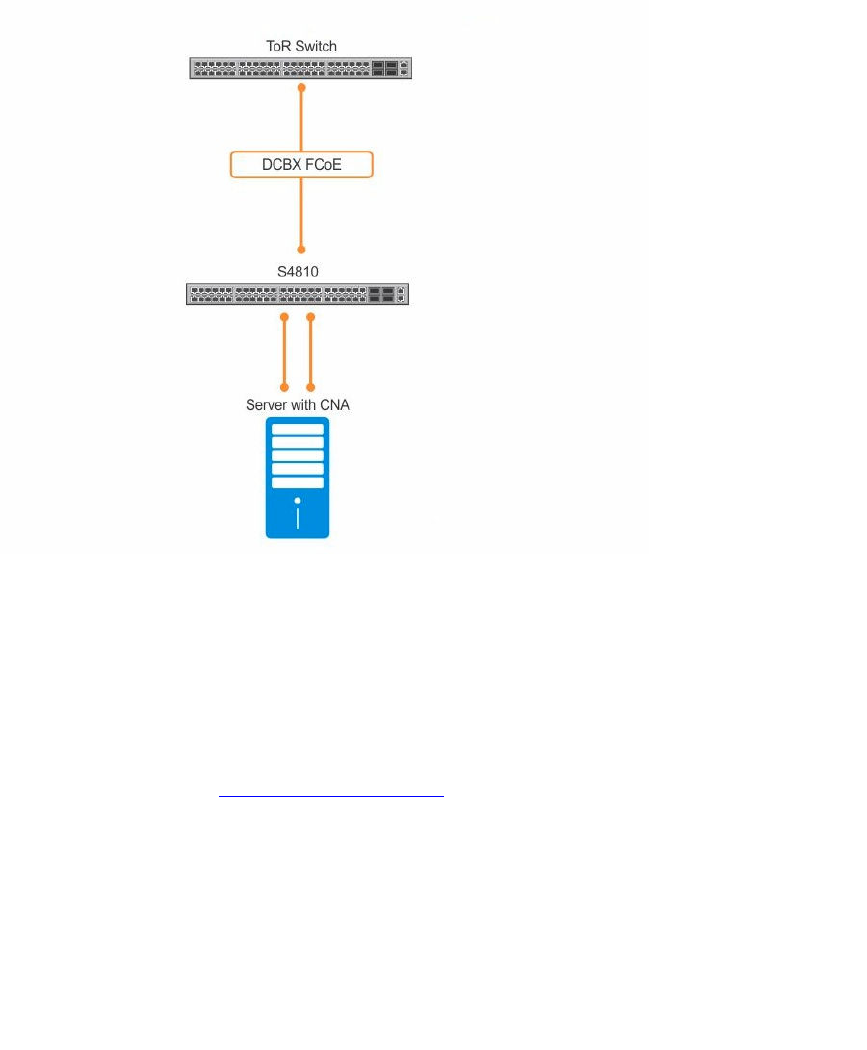
The following illustration shows a switch used as a FIP snooping bridge for FCoE traffic between an
ENode (server blade) and an FCF (ToR switch). The ToR switch operates as an FCF and FCoE gateway.
Figure 35. Configuration Example: FIP Snooping on a Switch
In this example, DCBx and PFC are enabled on the FIP snooping bridge and on the FCF ToR switch. On
the FIP snooping bridge, DCBx is configured as follows:
• A server-facing port is configured for DCBx in an auto-downstream role.
• An FCF-facing port is configured for DCBx in an auto-upstream or configuration-source role.
The DCBx configuration on the FCF-facing port is detected by the server-facing port and the DCB PFC
configuration on both ports is synchronized. For more information about how to configure DCBx and
PFC on a port, refer to the Data Center Bridging (DCB) chapter.
The following example shows how to configure FIP snooping on FCoE VLAN 10, on an FCF-facing port
(1/5/1), on an ENode server-facing port (1/1/1), and to configure the FIP snooping ports as tagged
members of the FCoE VLAN enabled for FIP snooping.
Example of Enabling the FIP Snooping Feature on the Switch (FIP Snooping Bridge)
Dell(conf)# feature fip-snooping
Example of Enabling FIP Snooping on the FCoE VLAN
Dell(conf)# interface vlan 10
Dell(conf-if-vl-10)# fip-snooping enable
340
FCoE Transit


















