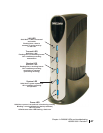
• Glossary
1033295-0001 Revision 2
63
Glossary
D
E
H
I
IP address - a 32-bit number that identifies each
sender or receiver of information that is sent in
packets across the Internet. An IP address has two
parts: the identifier of a particular network on the
Internet and an identifier of the particular device
(which can be a server or a workstation) within
that network. On the Internet itself - that is,
between the router that move packets from one
point to another along the route - only the network
part of the address is looked at.
Dotted decimal notation - An IP address
consists of 32 bits. Rather than working with 32
bits at a time, it is a common practice to segment
the 32 bits of an IP address into four 8-bit fields
called octets. Each octet is converted to a
decimal number (the Base 10 numbering
system) in the range 0-255 and separated by a
period (a dot).
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) -
a communications protocol that lets network
administrators manage centrally and automate
the assignment of Internet Protocol (IP)
addresses in an organization's network.
.
Enterprise - an entity autonomously operating a
network using TCP/IP and in particular
determining the addressing plan and address
assignments within that network.
Host - In packet- and message-switching
communications networks, the collection of
hardware and software that makes use of packet
or message switching to support user-to-user,
i.e., end-to-end, communications, interprocess
communications, and distributed data
processing. More simply, any computer that has
full two-way access to other computers on the
Internet.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) -
the organization that has overseen the allocation
of Internet Protocol addresses to Internet service
providers (ISPs).
Internet protocol (IP) - The method or protocol
by which data is sent from one computer to
another on the Internet. Each computer (known
as a host) on the Internet has at least one IP
address that uniquely identifies it from all other
computers on the Internet. The protocol within
TCP/IP that governs the breakup of data
messages into packets, routing the packets from
sender to destination network and station, and
reassembling the packets into the original data
messages at the destination.
Internet service provider (ISP) - A business that
supplies Internet connectivity services to
individuals, businesses, and organizations.
Some ISPs are large national or multinational
corporations that offer access in many locations,
while others are limited to a single city or
region.