118 Hardware Maintenance Manual: xSeries 250
• Eight physical drives are supported in an array if the stripe-unit size is set
to 32 KB or 64 KB.
• Sixteen physical drives are supported in an array if the stripe-unit size is
set to 8 KB or 16 KB.
If you are using the ServeRAID-3H or ServeRAID-3HB, sixteen physical drives
are supported in an array if the stripe-unit size is set to 32 KB or 64 KB.
Supported RAID levels
Disk arrays are used to improve performance and reliability. The amount of
improvement depends on the application programs that you run on the server, the
RAID levels that you assign to the logical drives, and the stripe-unit size.
The ServeRAID controllers support RAID level-0, RAID level-1, RAID level-1
Enhanced (1E), RAID level-5 and RAID level-5 Enhanced (5E).
Understanding RAID level-0
RAID level-0 stripes the data across all the drives in the array. This offers substantial
speed enhancement, but provides for no data redundancy. RAID level-0 provides the
largest capacity of the RAID levels offered, because no room is taken up for redundant
data or data-parity storage.
RAID level-0 requires a minimum of one drive and, depending upon the level of
firmware and the stripe-unit size, supports a maximum of eight or 16 drives.
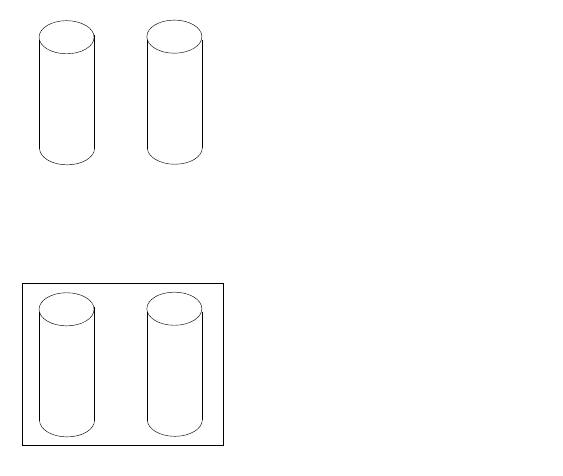
The following illustration shows an example of a RAID level-0 logical drive.
You start with two physical drives.
Create an array using the two physical drives.
Then, create a logical drive within that array.


















