122 Hardware Maintenance Manual: xSeries 250
With RAID level-1E, if one of the physical drives fails, the ServeRAID controller
switches read and write requests to the remaining functional drives in the RAID level-
1E array.
Understanding RAID Level-5
RAID level-5 requires a minimum of three physical drives. This RAID level stripes
data and parity across all drives in the array. When an array is assigned RAID level-5,
the capacity of the array is reduced by one drive (for data-parity storage).
RAID level-5 is generally the most desirable choice, because it offers both data
protection and increased throughput. RAID level-5 gives you higher capacity than
RAID level-1, but RAID level-1 offers better performance.
The RAID level-5 requires a minimum of three drives and, depending upon the level
of firmware and the stripe-unit size, supports a maximum of eight or 16 drives.
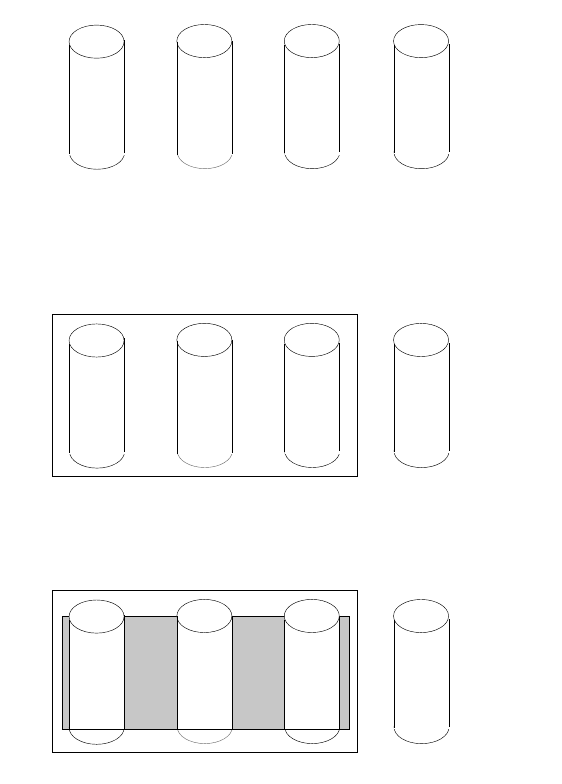
The following illustration is an example of a RAID level-5 logical drive.
You start with four physical drives.
Create an array using three of the physical drives, leaving the fourth as a hot-spare
drive.
Then, create a logical drive within that array.
The data is striped across the drives, creating blocks. Notice that the storage of the
data parity (denoted by ★ ) also is striped, and it shifts from drive to drive.
x
x
x


















