D8B Manual • Chapter 4 • page 115
MIDI and the D8B
MIDI Basics
Your Digital 8•Bus works very well when
incorporated in a MIDI network, utilizing a computer
referenced to time code.
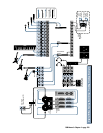
Be sure to connect the D8B MIDI jacks to your
MIDI interface. Within your computer-based MIDI
sequencer, set the MIDI channel connected to the
D8B to transmit MIDI Time Code (MTC). This is
necessary to run automation from a Digital Audio
Workstation (DAW).
MIDI
OUT
MIDI
IN
MIDI Interface
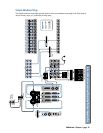
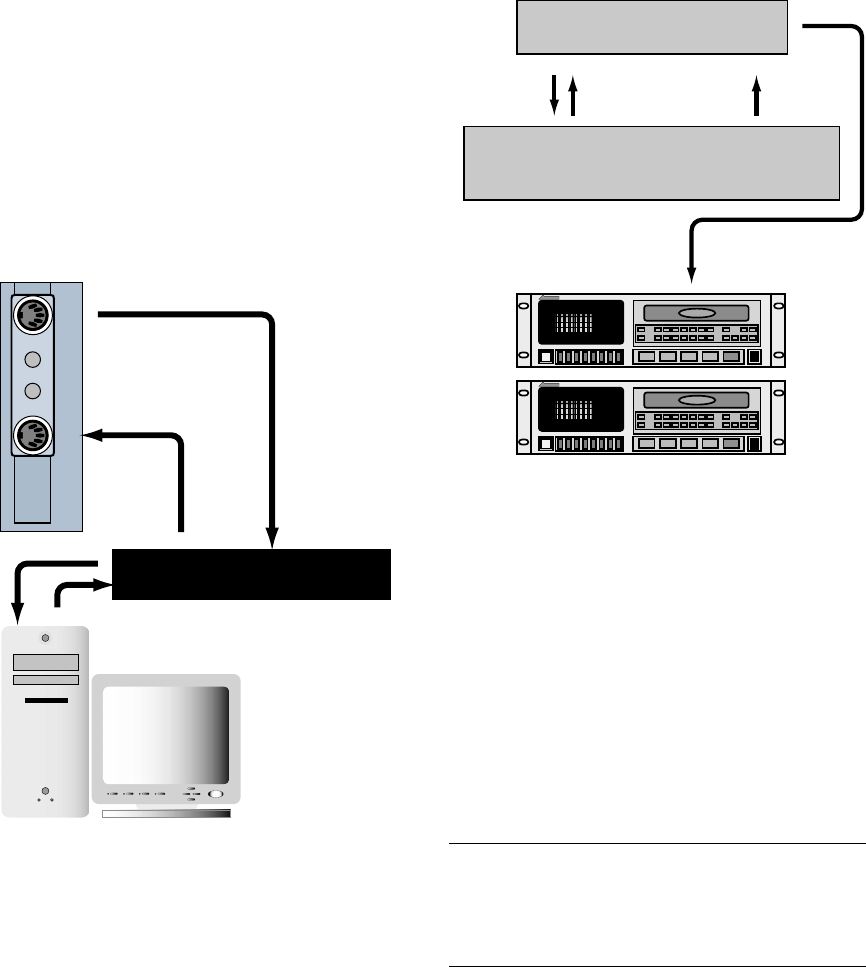
When you don’t include a computer in your setup,
you need a device like the Alesis BRC to transmit
MTC to the D8B for time reference when performing
dynamic and snapshot automation.
Modular Digital Multitrack
Modular Digital Multitrack
BRC
Digital 8•Bus
MIDI SYNC
SYNC
The Digital 8•Bus provides control over some key
MIDI parameters. These parameters affect your
system’s ease of use and efficiency, and should be
verified:
• MMC DEVICE ID: Some 8-track digital recorders
require that you define the device ID numbers
used for each recorder in the MIDI Machine
Controller. Typically, tracks 1–8 are device 0,
tracks 9–16 are device 1, and tracks 17–24 are
device 2, so these are the default settings.
• ONE BUTTON PUNCH: You can also select
whether to press the PLAY and RECORD buttons
to enter record mode, or just press the RECORD
button (One Button Punch).
Note: We recommend leaving One Button Punch off to
provide an extra measure of safety in case you
inadvertently press the RECORD button in the
Transport Section.
• MTC OFFSET: MIDI File Offset can be used to
indicate the starting time deviation of a Standard
MIDI File (SMF), referenced to absolute time code.
• TEMPO MAP: If you use a sequencer in your
recording process, you can create a standard
MIDI file from the song(s) you’ve recorded. Copy
the tempo map from the SMF to the Digital 8•Bus
and “synchronize” the D8B display to the
Bars:Beats:Ticks of the sequenced program.
SMFs are loaded from the floppy disk drive.