Routing Information 201
Access Server Administrators’ Reference Guide 16 • IP
Gateway (RouteGateway)
Specifies the IP address to which the packets should be forwarded.
Cost (RouteCost)
This is the cost of the route as defined by RIP standards. Cost is sometimes considered to be number of hops.
A cost of 16 is considered to be infinite. A cost can be given to user-entered routes so their preference in rela
-
tion to learned routes can be calculated.
Interface (ipRouteIfIndex)
The index value that identifies the local interface through which the next hop of this route should be reached.
The interface identified by a particular value of this index is the same interface as identified by the same value
of ifIndex.
State (RouteState)
• invalid(1)—This setting deletes the route.
• active(2)—A valid route is in use.
• nopath(3)—No route is available to the specified gateway. The gateway is not known to local networks.
• agedout(4)—Invalid route (soon to be removed).
• costly(5)—A valid route, but not in use because of it’s higher cost.
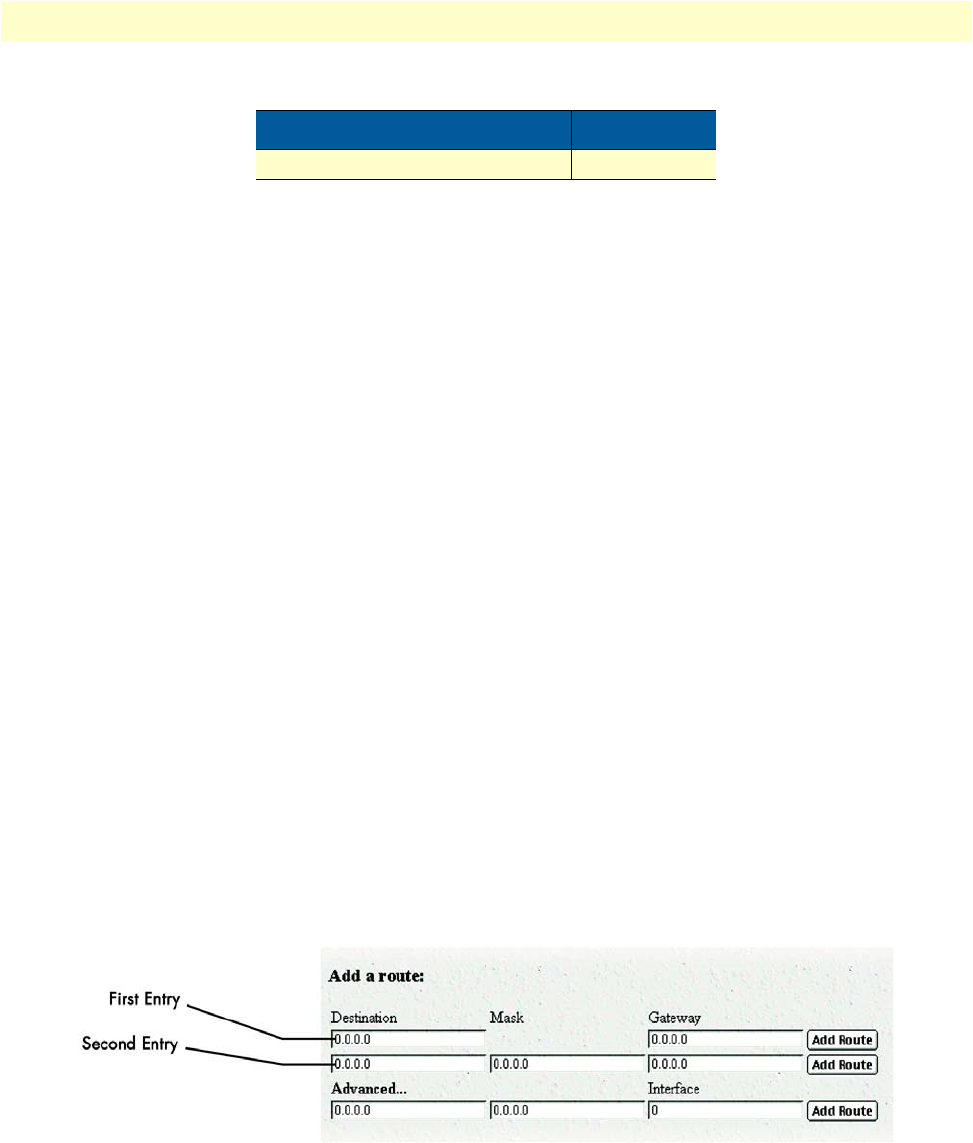
Add a route:
This portion of the IP Routing Information window is where you can add a new route to the IP Routing Infor-
mation table. The first entry (see figure 84) can be used to add or change the default gateway or as a short-cut
to creating a point-to-point connection. The second entry under
Add a route:
(see figure 84) is where static
routes to remote networks or a specific remote host are created.
Figure 84. Add a route portion of IP Routing Information window
Adding the default gateway
Do the following:
255.255.255.0 class-C
Table 3. Masks
Mask Network


















