109
with the standard resolution of 60 dots per inch (dpi).
The command to print normal density (60 dpi horizontally, 72
dpi vertically) uses this format:
(ESC) “*”
CHR$(0) YZ~7z2ml mz .....
(ESC) “*” specifies the graphics mode, the CHR$(0) specifies
normal density. Other densities are described later. Any
number of graphics data may follow; the nl and n2 specify the
number of bytes.
To figure the value of nl and n2, you need to work out how
wide your image will be. Because you are limited to the largest
number that can be sent in one byte (255), the formula to work
out
nl and n2 is:
if the number of columns is X,
then nl =X MOD 256, and n2=INT(X/256)
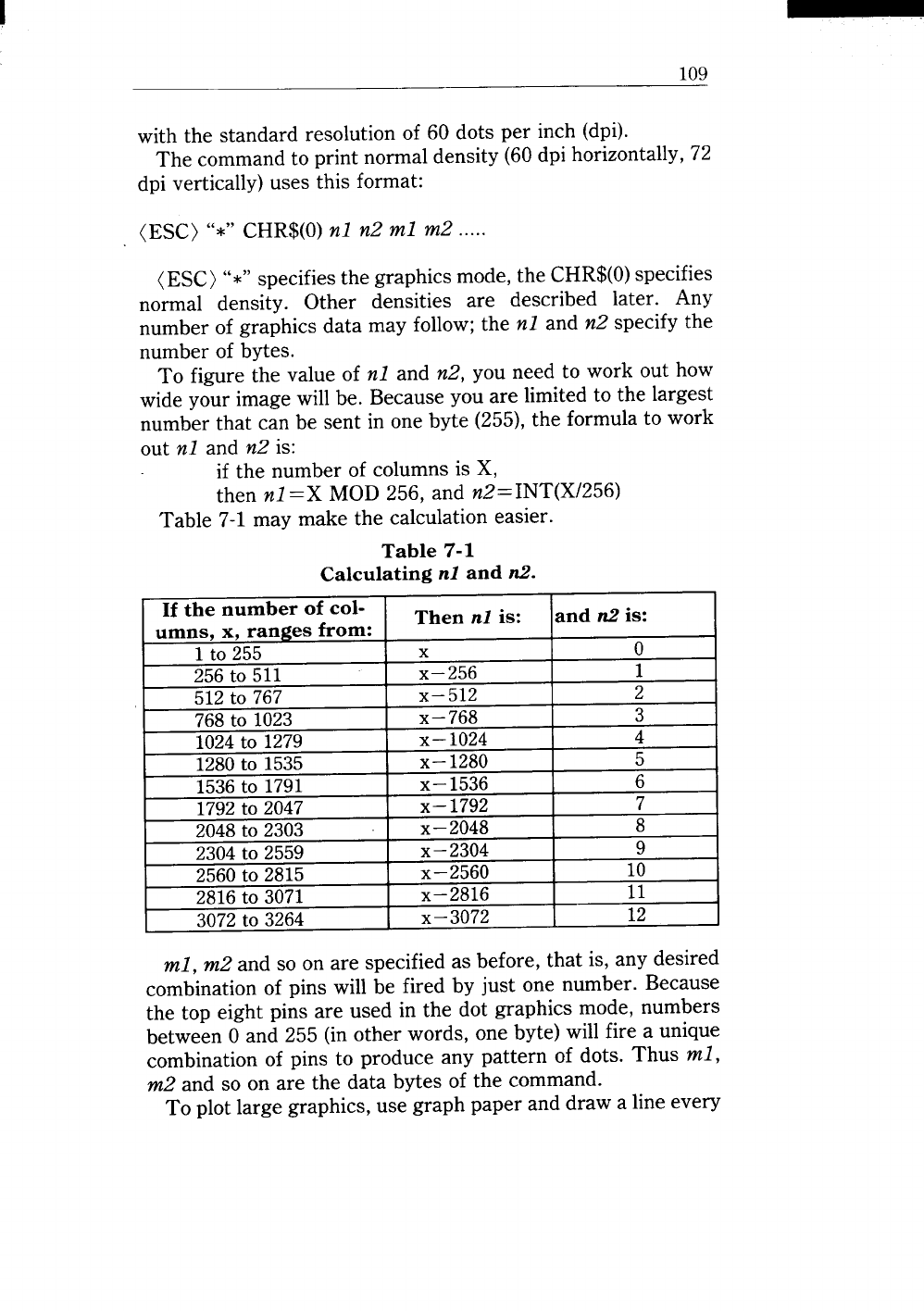
Table 7-1 may make the calculation easier.
Table 7-1
Calculating nl and n2.
If the number of col-
Then
nl is:
umns, x, ranges from:
and n2 is:
1 to
255
x
o
256
to 511
x—256
1
512 to 767
X– 512
2
768 to 1023
x—768
3
1024 to 1279
X— 1024
4
-1
’30n t,.
–
1280
5
X— 1536
6
1I~~
L“ L . .
X– 1792
7
2048to 2303
x–2048
8
““’34to 2559
x–2304
9
2815
x—2560
10
llc’1,P
11
l&OU LU 1535
x
1536to 1791
I 709 +n 2047
m.... ,.-..,., ,,
-m,-,
..
cln79
19
I
Lo lo LO m) I 1
I
A LIULU
3072to 5L04
I
ii— au 1L
I
.-
I
ml, m2 and so on are specified as before, that is, any desired
combination of pins will be fired by just one number. Because
the top eight pins are used in the dot graphics mode, numbers
between Oand 255 (in other words, one byte) will fire a unique
combination of pins to produce any pattern of dots. Thus ml,
m2 and so on are the data bytes of the command.
To plot large graphics, use graph paper and draw a line every


















