18
STP2002QFP
Sun Microelectronics
Fast Ethernet, Parallel Port, SCSI (FEPS) - STP2002QFP
when the peripheral device cannot receive another byte of data. P_BSY
(PP_BSY) is sampled before data strobe becomes active and after data strobe
becomes inactive, to ensure that a data transfer is not attempted while the de-
vice is busy.
It is this mode, which provides the fastest transfer of data over the inter-
face, the fastest cycle time is six SBus clocks per byte. This transfer time is
arrived at as follows: DSS=0, DSW=3 (minimum width of DSW is three
SBus clocks), and three SBus clocks between consecutive data strobes. This
assumes that P_BSY (PP_BSY) is not asserted during the transfer cycle. Ref-
erence Figure 2.
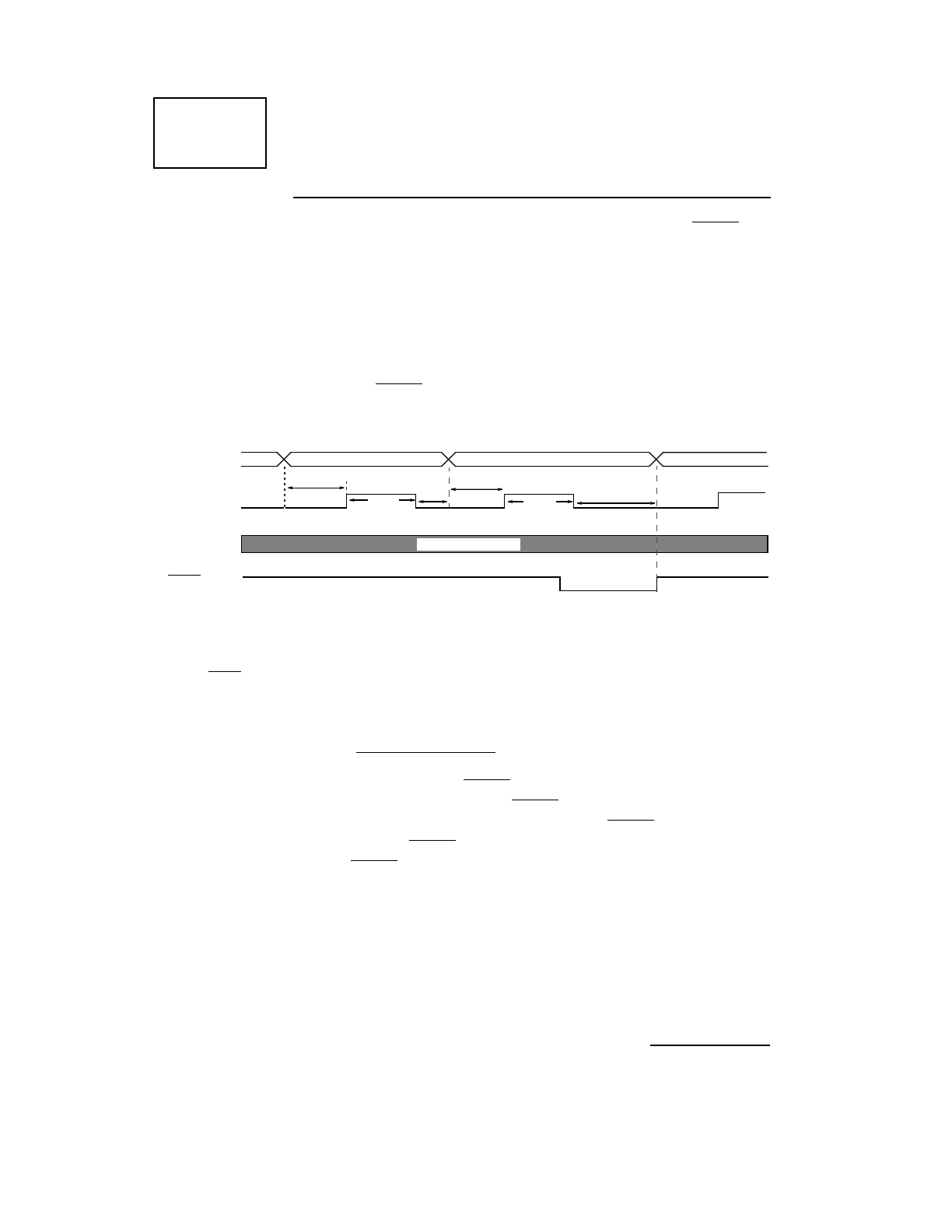
Figure 2.
4.3.1.1.2 Handshake with Ack: BUSY_OP=0, ACK_OP=1)
Data transfers are controlled by the use of P_D_STRB (PP_STB), P_ACK
(PP_ACK), and optionally P_BSY (PP_BSY). P_ACK (PP_ACK) is re-
quired for each byte transferred. If P_BSY (PP_BSY) is active at the end of
the cycle, further data transfers will be gated until P_BSY (PP_BSY) be-
comes inactive. If P_BSY (PP_BSY) is not present, then data transfers will
proceed. P_BSY (PP_BSY) is also sampled immediately before P_D_STRB
(PP_STB) is generated to ensure that a data transfer is not attempted while the
device is busy. Reference the data transfer diagram in Figure 3.
P_DATA (O)
P_D_STRB (O)
1
2
3
1
2
5
4
P_ACK (I)
P_BSY (I)
DSS
DSS
DSW
DSW
Don’t Care
1. Data setup as defined in the hardware configuration register.
2. Data strobe width as defined in the hardware configuration register.
3. There is a three SBus clock delay from the end of data strobe to the next byte of data being clocked onto the P_DATA
bus.
4. Acknowledge is a don’t care condition for all data transfers.
5. When
P_BSY is active, it gates further data transfers.


















