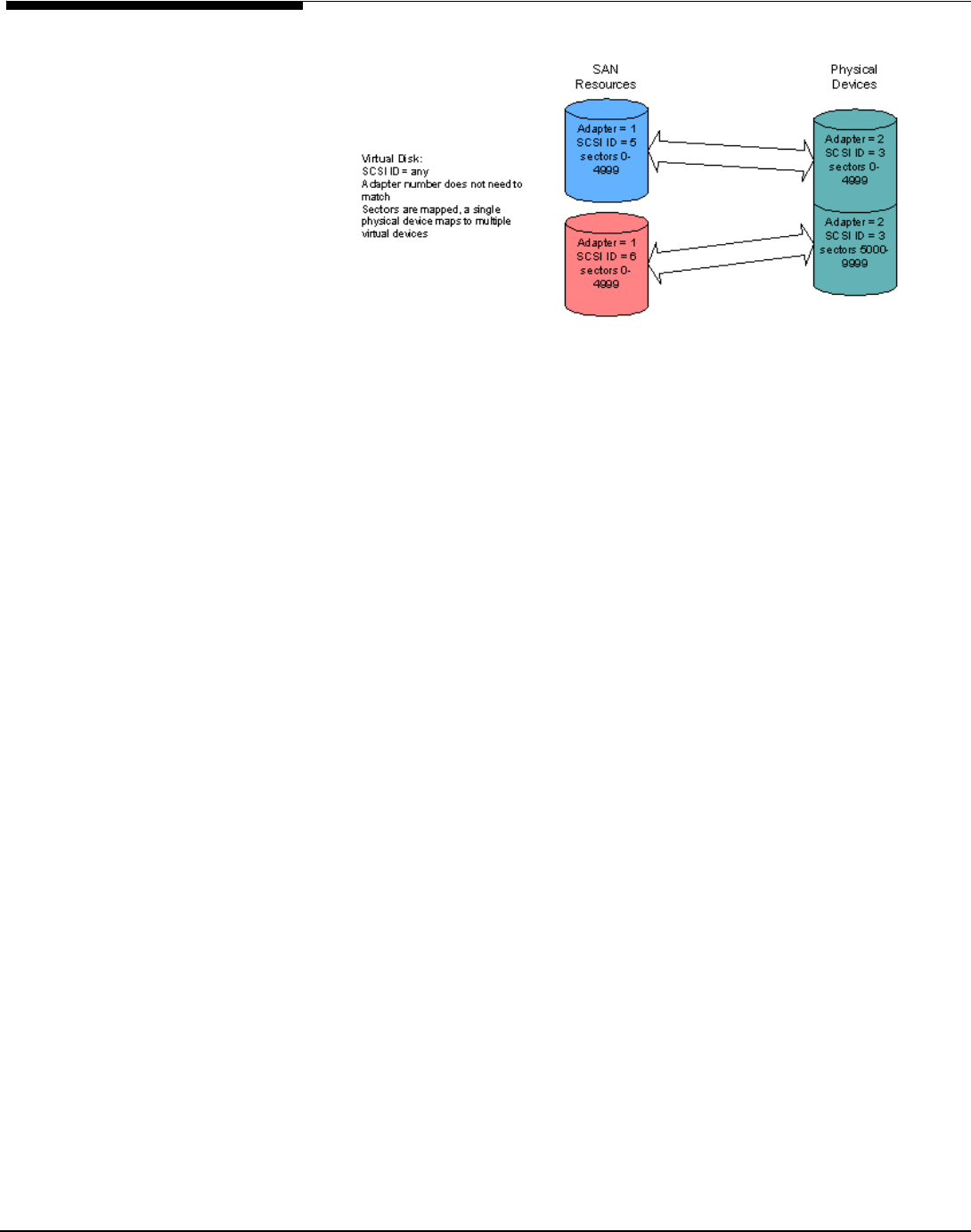
This example shows a single physical disk split into two virtual devices. This is
useful when a single large device exists, such as a RAID, which could be shared
among multiple client application servers.
Virtual devices can be created using various combining and splitting methods,
although you will probably not create them in this manner in the beginning.
You may end up with devices like this after growing virtual devices over time.
Direct devices
Direct devices are directly mapped SCSI devices. Direct devices can be created
from hard disks, tape drives, device libraries, JBODs, and RAID cabinets.
Because they are not virtualized, direct devices cannot take advantage of ASC’s
advanced storage management options, such as mirroring or snapshot copy.
Direct devices, such as tape drives, device libraries, JBODs, and RAID cabinets,
can be used to back up data on your storage network.
A characteristic of some application software, such as backup tools and devices,
require that they address the SCSI ID directly. This is true for library devices and
the drives within the library; the software uses the SCSI IDs to address the
library and drives. For this reason, direct devices use fixed SCSI IDs that cannot
be changed.
Designating a hard drive as a direct device can be useful for data migration
into ASC. Data on an existing disk can be brought into ASC as a direct device.
The data can then be copied using Linux’s dd command to a virtualized disk
that does not contain any data or have any clients attached so that it can take
advantage of ASC’s virtualization and advanced storage management options.
Acer Altos® NAS 700 Solution Guide
75