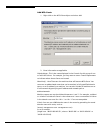
File System
- ASC automatically detects the file systems supported by the
system. If the server has the required ACL rpms installed,
XFS
will appear in the
list; otherwise only
EXT3
and
EXT2
will appear.
Block Size
- The minimum amount of space to use for each file. For example, if
you keep the default of 4, each file will minimally be 4k in size.
Synchronous File I/O
- Provides file system caching. If selected, there will be no
file system caching. This offers greater data integrity but impacts performance.
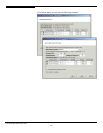
Journaling Mode
- (Linux EXT3 only) Specifies the journaling mode for file data.
Metadata is always journaled.
-
ournal:
All data is committed into the journal prior to being written into the
main file system.
J
-
Ordered:
This is the default mode. All data is forced directly out to the main
file system prior to its metadata being committed to the journal.
-
Writeback:
Data ordering is not preserved. Data may be written into the main
file system after its metadata has been committed to the journal. This is said to
be the highest-throughput option. It guarantees internal file system integrity,
but it can allow old data to appear in files after a crash and journal recovery.
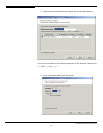
Confirm that all information is correct and then click
Finish
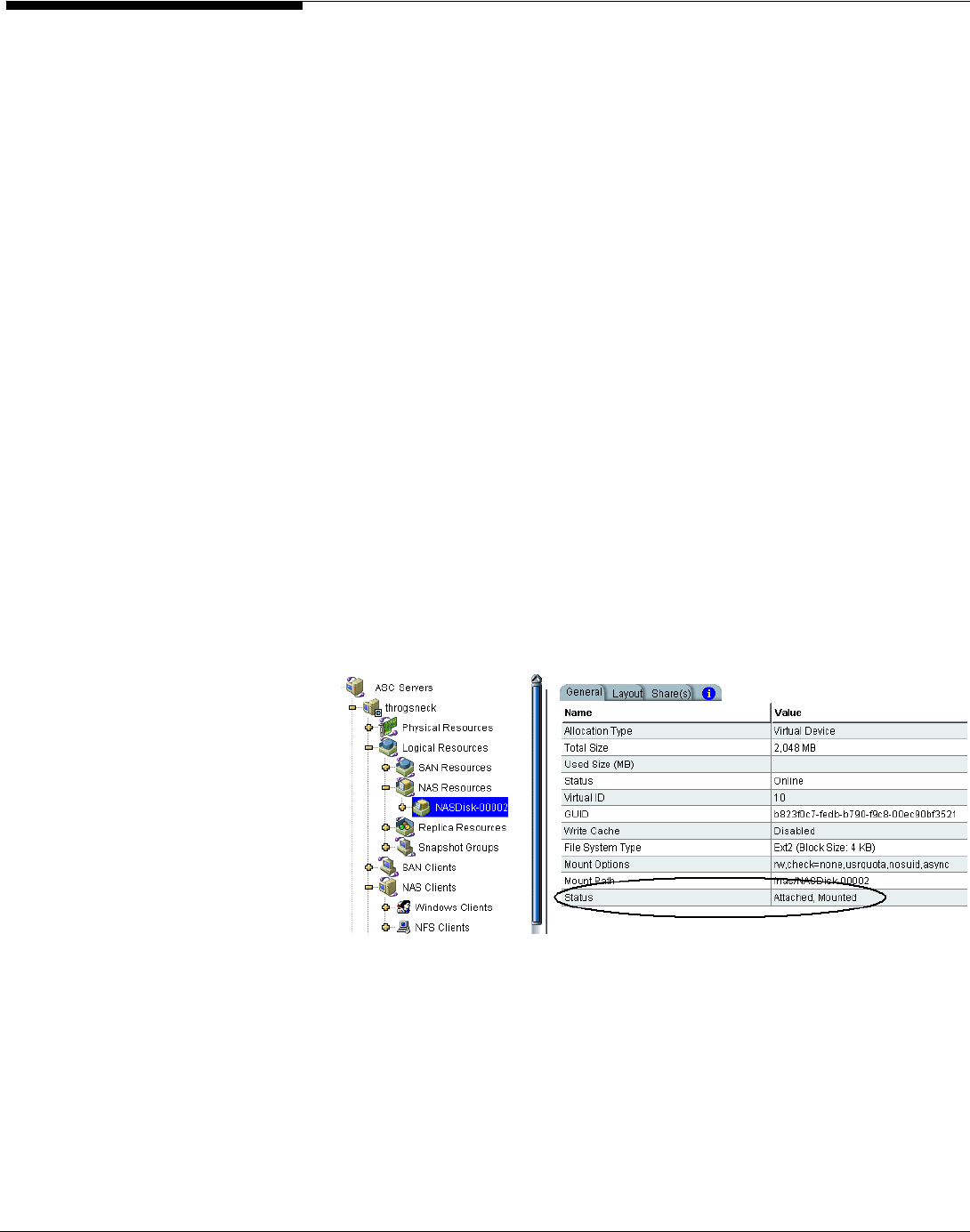
to create the NAS
Resource. You should wait until the NAS Resource is attached and mounted
before continuing with folder assignments.
NOTE: After creating your ASC NAS resources, check the ASC Server for the
following file: /etc/group
cat the /etc/group file and note the number for the
nasgrp
.
When using NFS-mounted ASC NAS Resources, log in with a user account that is
a member of the group number for
nasgrp
.
Acer Altos® NAS 700 Solution Guide
138