TELEPHONE INTERFACE MODULE (TIM)
14-3
14.1.5 TELEPHONE LINE STYLES
There are several different styles of telephone
lines the TIM controls. The following styles of lines
and their basic connection are supported.
1. Direct Inward Dialing (DID)
The DID offers direct inward dialing of the tele-
phone number and supplies the -48V DC battery
voltage to the incoming lines. The Central Office
(CO) contacts the DID by closing the loop and sends
the number to the DID by dial pulse or DTMF. The
DID can handle 2, 3 or 4 digits being spilled forward
by the CO.
2. 4-Wire E&M
4-Wire E&M is primarily used with electronic
switches, public leased lines or microwave equip-
ment to provide complete separation of transmit and
receive audio lines. The signaling unit provides the
-48V DC battery to the M-Lead, while the trunk unit
provides ground to the M-Lead. The signaling is
reversed for the E-Lead (see Section 14.2).
3. Dial Pulse
Dial pulsing is the "break and make" of the loop path
current to cause no flow and flow. The number of
breaks, when no current flows, is the number of the
desired digit, with 10 pulses equaling 0.
4. Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF)
DTMF tone signaling is used on almost all push
button telephones. DTMF is where the desired digit
is composed of a combination of two tones. A tone
pair consists of one tone from the low band group
(697, 770, 852 or 941 Hz), and the high band group
(1209, 1336, 1447 or 1633 Hz).
14.1.6 AUDIO PROCESSING
The audio processing converts intra-terminal
voice path audio to be placed on the telephone lines.
The telephone line interface contains a hybrid that
transmits and receives audio from the telephone line
and keeps the transmitted audio out of the received
audio to eliminate sidetone and echoing. The hybrid
also converts the balanced telephone line to unbal-
anced connections.
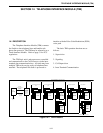
14.1.7 RECEIVE AUDIO
The receive audio is from the telephone line and
processed for the intra-terminal Pulse Code Modula-
tion (PCM) channel stream (see Figure 14-14). The
received audio has three paths:
1. Voice Audio
The receive audio from the telephone line comes
from the unbalanced receive side of the hybrid. The
audio is level adjusted through an amplifier to give
a correct line level adjustment and passes through
minimal filtering to eliminate the possibility of
unwanted frequencies. A transmission gate turns
the audio on and off toward the terminal. The gate
is followed by a level adjustment amplifier/buffer
before the audio enters the intra-terminal voice
processing. The intra-terminal voice processing is a
PCM CODEC with a time slot determination circuit.
The CODEC digitizes the analog voice and outputs
it onto the PCM transmit channel stream in the
appropriate time slot. The master clock and master
frame sync are inputs to the TIM. These inputs
provide timing for the CODEC and timing determi-
nation circuit.
2. Dial Tone Detection
The receive audio from the telephone line is taken
from the line level adjust amplifier buffer and passes
into a bandpass filter centered on the frequencies
used for dial tone. The bandpass filter is adjusted
for detection of the dial tone sent by the CO. The
output of the bandpass filter passes to a rectification
and detection circuit. The output of the detection
circuit indicates the presence of dial tone to the logic
unit.
3. DTMF Detection
The receive audio from the telephone line is taken
from the line level adjust amplifier buffer. The
audio passes into the DTMF detection circuitry and
outputs the tone pair received and the valid tone pair
signal to the logic unit.