affecting the
PSW,RB
registers
or
accumulator. When
one takes into account that registers R
7-RO
and the
accumulator can be Direct Addressed, the two-operand
logic operations allow the destination (first operand) to
be a byte
in
the Internal Data RAM, a Special Function
Register, RB registers
(R
7-RO)
or
the accumulator while
the choice
of
the second operand can
be
any
of
the
aforementioned or an immediate value. The
8051
can
also perform a logical or,
or
a logical and, between the
Boolean accumulator (i.e. the carry flag) and any bit,
or
its complement, that can be accessed through Direct
Addressing. The and, or, and exclusive-or logic opera-
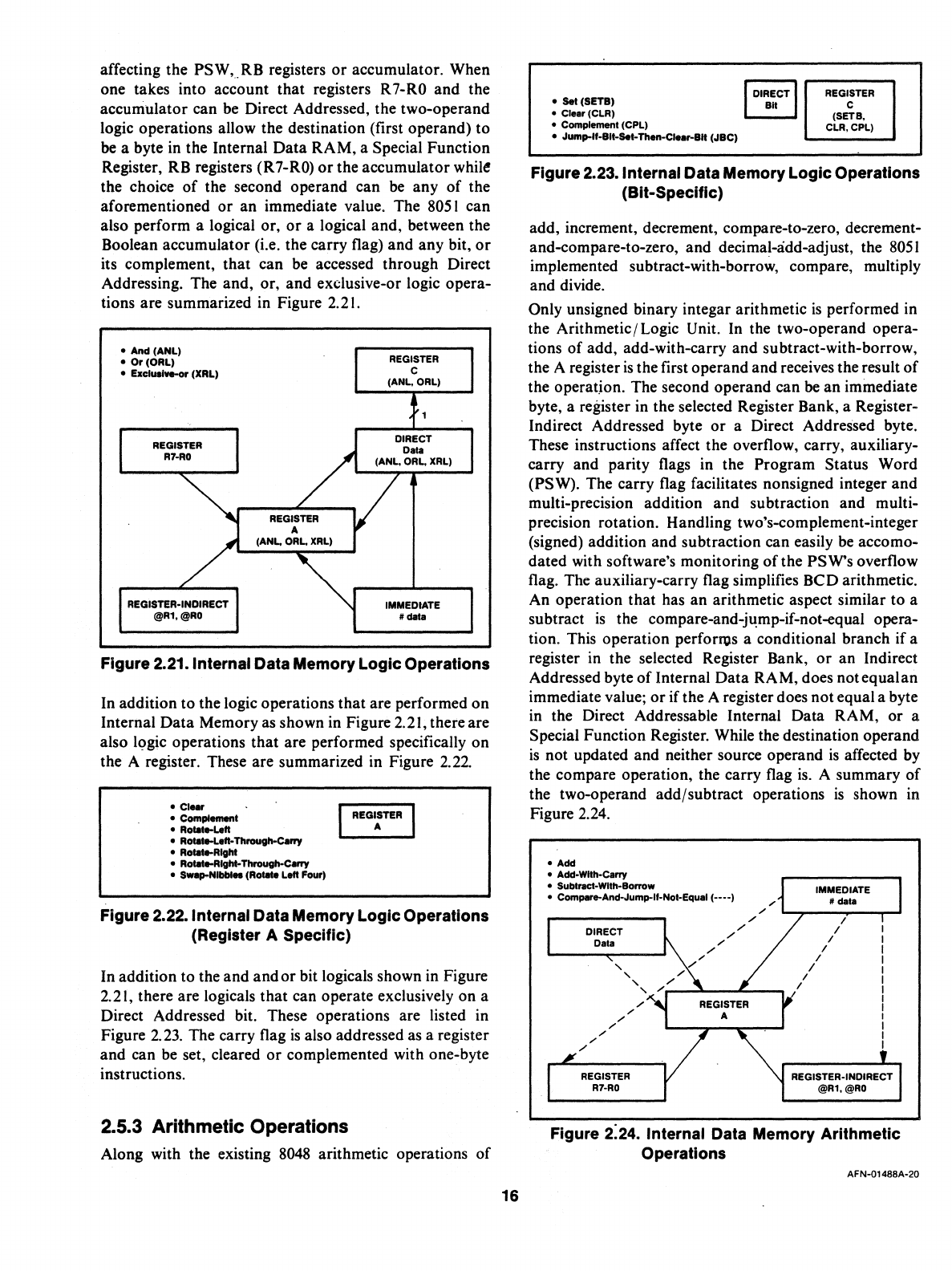
tions are summarized in Figure 2.21.
• And
(ANL)
.Or(ORL)
• Exclusive-or (XRL)
IMMEDtATE
# data
Figure 2.21. Internal Data Memory
Logic
Operations
In addition to the logic operations that are performed on
Internal
Data
Memory as shown in Figure 2.21, there are
also logic operations that are performed specifically on
the A register. These are summarized in Figure
2.22.
• Clear
• Complement
•
Rotate-Laft
• Rotate-Laft-Through-Carry
• Rotate-Right
• Rotate-Rlght-Through-Carry
• Swep-NlbbI
..
(Rotate Left Four)
REGISTER
A
Figure 2.22. Internal Data Memory
Logic
Operations
(Register A Specific)
In addition to the and
andor
bit logicals shown in Figure
2.21, there are logicals that can operate exclusively on a
Direct Addressed bit. These operations are listed in
Figure 2.23. The carry flag
is
also addressed
as
a register
and can
be
set, cleared
or
complemented with one-byte
instructions.
2.5.3 Arithmetic Operations
Along with the existing
8048
arithmetic operations of
16
•
Set(SETB)
• Clear
(ClR)
• Complement (CPL)
• Jump-It-BII-Set-Then-Clear-BII (JBC)
REGISTER
C
(SETB,
ClR,CPL)
Figure 2.23. Internal Data Memory
Logic
Operations
(Bit-Specific)
add, increment, decrement, compare-to-zero, decrement-
and-compare-to-zero, and decimal-add-adjust, the
8051
implemented subtract-with-borrow, compare, mUltiply
and divide.
Only unsigned binary integar arithmetic
is
performed in
the ArithmetiC/Logic
Unit. In the two-operand opera-
tions of add, add-with-carry and subtract-with-borrow,
the A register
is
the first operand and receives the result
of
the operatjon. The second operand can be an immediate
byte, a register
in
the selected Register Bank, a Register-
Indirect Addressed byte or a Direct Addressed byte.
These instructions affect the overflow, carry, auxiliary-
carry and parity flags in the Program
Status Word
(PSW). The carry flag facilitates nonsigned integer and
multi-precision addition and subtraction and multi-
precision rotation. Handling two's-complement-integer
(signed) addition and subtraction can easily
be
accomo-
dated with software's monitoring
ofthe
PSWs
overflow
flag. The auxiliary-carry flag simplifies BCD arithmetic.
An operation that has an arithmetic aspect similar to a
subtract
is
the
compare-and-j~mp-if-not-equal
opera-
tion. This operation
perforros a conditional branch if a
register in the selected Register Bank,
or
an Indirect
Addressed byte of Internal Data RAM, does not equal an
immediate value;
or
if the A register does not equal a byte
in the Direct Addressable Internal Data RAM, or a
Special Function Register. While the destination operand
is
not updated and neither source operand
is
affected
by
the compare operation, the carry flag
is.
A summary of
the two-operand add/subtract operations
is
shown in
Figure 2.24.
• Add
• Add-With-Carry
• Subtract-With·Borrow
• Compare-And-Jump-II·Not·Equal
(
••••
)
DIRECT
Data
"
"
,
,
'"
,/
,/
,/
,/
,/
'"
REGISTER
R7·RO
REGISTER·INDIRECT
@Rl,@RO
Figure 2:24. Internal Data Memory Arithmetic
Operations
AFN·01488A·20