2 – General Description
Supported Network Configurations
2-8 SN0054628-00 A
Q
2.3.3.1
How the Solution Protects Against Failures
The following tables provides a list of common failure points in a network and the
corresponding protection that this high-availability solution provides.
2.3.3.2
Setup Requirements
To configure a high-availability solution using SVM appliances and SANbox SSPs,
you must make sure that:
■ Each HBA sees only one SANbox SSP.
■ Each host sees both SANbox SSP in the high-availability solution, and no others.
■ Each StoreAge SVM appliance sees both SANbox SSPs.
■ Each StoreAge SVM appliance sees all storage ports.
■ If the storage includes dual-controller active/passive RAIDs, each SANbox SSP
is cross-connected with the controllers, which means that each SANbox SSP
must see both controllers in the RAID.
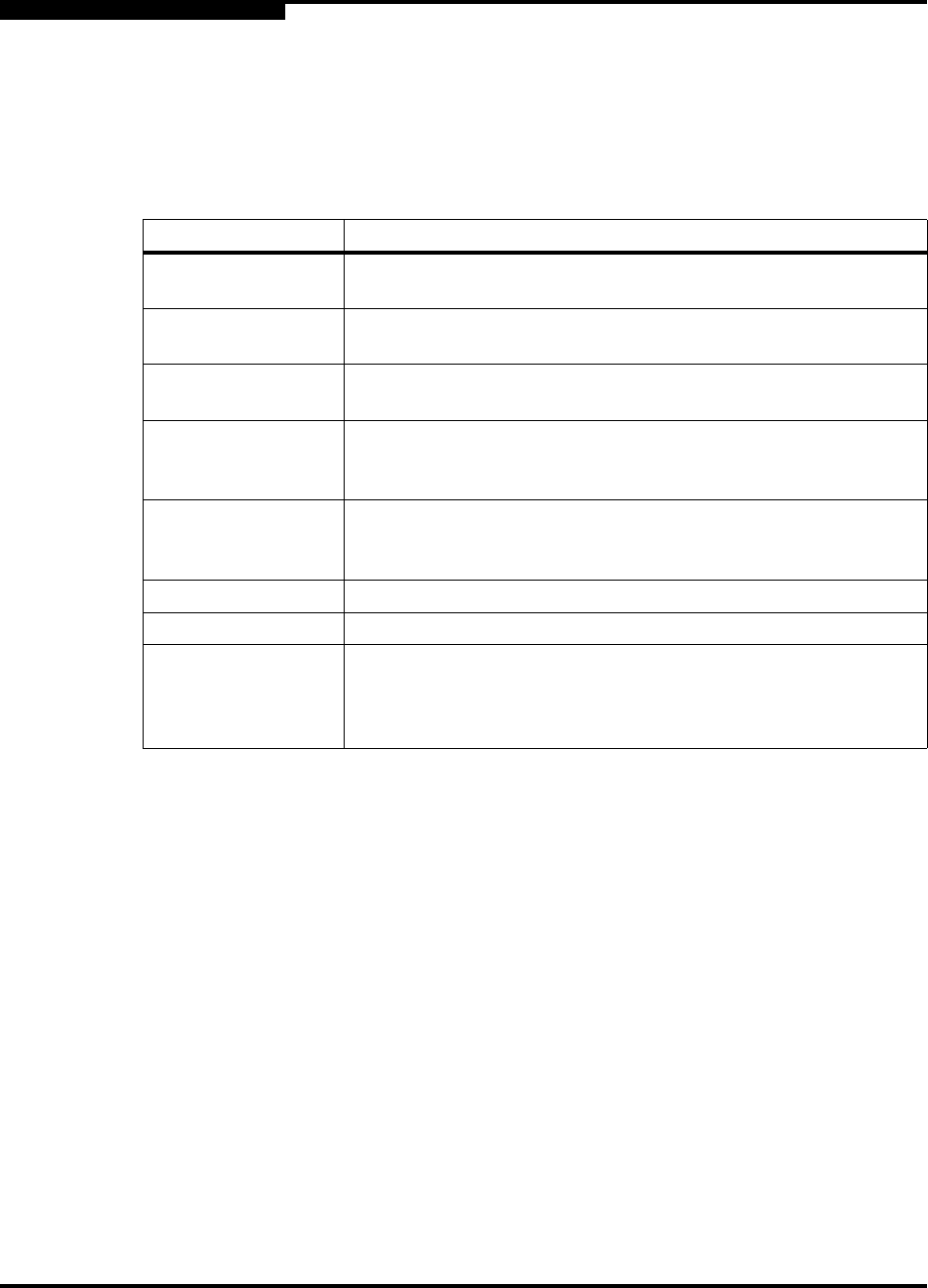
Table 2-1. High-Availability Solution Protection Against Network Failures
Failed Component: Protection:
HBA or path to
SANbox SSP
Host software uses a remaining HBA or path to the same SANbox
SSP
All HBAs or paths to
one SANbox SSP
Virtual volume becomes active on alternate SANbox SSP, host
software uses alternate HBA
One SANbox SSP Virtual volume becomes active on alternate SANbox SSP, host
software uses alternate HBA
One path between
one SANbox SSP
and storage
■ Back-side I/O uses alternate path
■ LUN uses alternate storage controller, if necessary
All paths between
one SANbox SSP
and storage
■ Virtual volume becomes active on alternate SANbox SSP
■ Host software uses alternate HBA
Storage controller
■ Back-side I/O uses path to alternate storage controller
SVM appliance Alternate SVM appliance takes over system management
One or more paths
between one SVM
and one SANbox
SSP
Alternate SVM appliance takes over system management
