Policy Manager - My Certificates
Issue 4 May 2005 241
About Certificate Usage (Exchange)
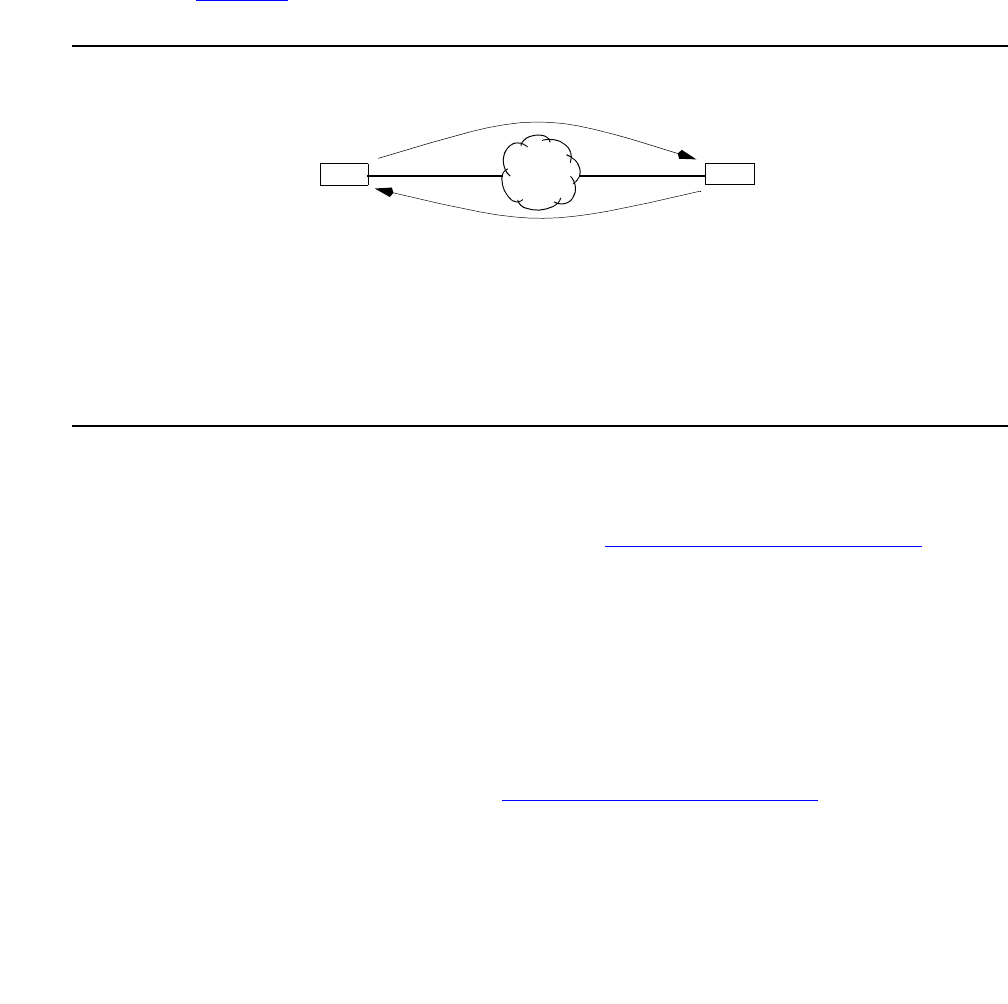
Every certificate identifies its owner and contains the owner’s public-key. The concept of
certificate usage is based on Owners and Targets. An owner sends its certificate to a target,
who then uses it to encrypt any information it sends to the owner. Owners and targets can be a
VSU, Remote Client, or any device that can use the Internet-Key Exchange (IKE) protocol to
exchange certificates.
The roles of owners and targets is purely based on point-of-view. Whenever a target needs to
receive encrypted traffic from an IKE compatible device, the target is viewed as an owner
because it must send its certificate to the IKE device. The concept of owners and targets is
illustrated in Figure 80
. It’s important to understand that a target must have an owner’s
certificate before it can send encrypted traffic to the owner.
Figure 80: Certificate exchange between VSUs
Assigning a Target for a Certificate
After a certificate is installed in a VSU (as described in Policy Manager - My Certificates on
page 234), it must be assigned a target.
A Bundle is used to define a certificate having a specific target type, address, description, and
queue position. The Policy Manager for IKE Certificate Usage lists all the bundles for a specific
VSU.
The Bundle Numbers identify which VSU Certificate is associated with the bundle. For example,
Bundle Number 3 means that VSU Certificate number 3 is associated with the bundle. Up to
eight bundles can be created, which directly relates to the number of signed certificates that can
be dynamically stored in a VSU. The certificates stored on a specific VSU can be viewed from
the Policy Manager for My Certificates (See Policy Manager - My Certificates
on page 234).
The target of a bundle is usually another VSU, but it can be any IKE compatible device. A target
can be configured as an IP address, VPN object, fully qualified domain name, e-mail address,
or director server name.
VS
WA
VS
Certificate
Certificate
Before VSUA can receive encrypted
traffic from VSUB, a certificate
owned by VSUA must be sent to VSUB
(the target of VSUA’s certificate).
The roles and process is reversed
when VSUB needs to receive
encrypted traffic from VSUA.
VSUA’s
Encrypted traffic to VSUA
A
B


















