Using Device tabs to configure the security gateway
Issue 4 May 2005 63
3. In the Memo text box, type in any information about the security gateway.
4. When finished, click Save.
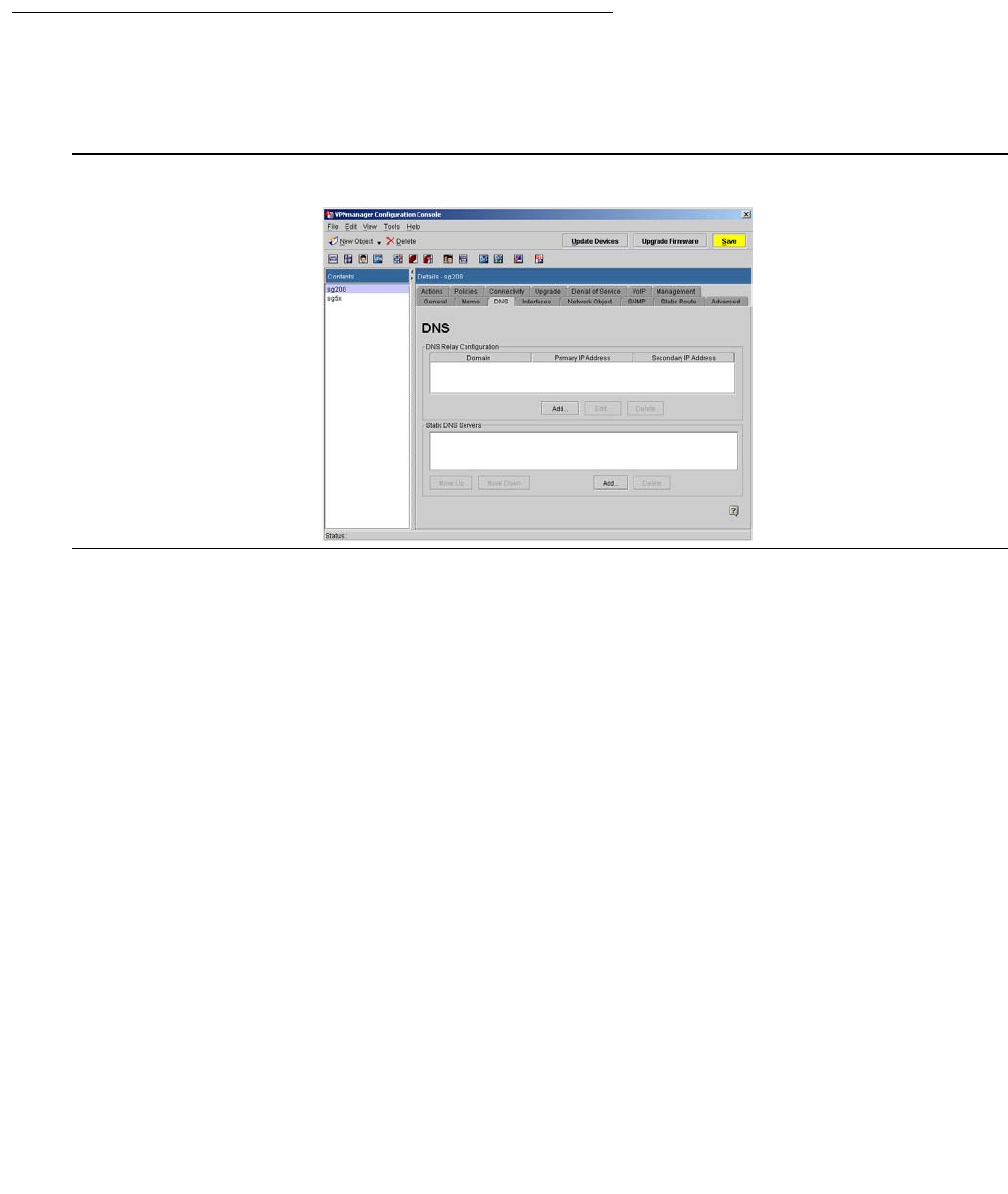
DNS tab
Use the DNS tab to define where to forward the Domain Name Service (DNS) name resolution
requests from the IP devices on the private side of the security gateway.
Figure 18: DNS tab
Configuring the DNS tab for security gateways at 4.3 or later
The security gateway includes a DNS name server, and accepts DNS queries from devices on
the private side. DHCP devices on the private side receive access to the DNS service
automatically. Non-DHCP devices must be manually configured to identify the security gateway
as their DNS server. The security gateway server maintains a DNS database on all DHCP
clients on the private interface. Non-DHCP clients have no DNS identity.
Note: The security gateway performs DNS relay functionality only for the private zone.
To resolve DNS queries, the security gateway first consults its own database. If this is
unsuccessful, the query is forwarded through the public interface. If DNS Relay Configuration
domain entries exist, the security gateway tries to find the match of the DNS request domain
with the entries’ domains. If a match is found, the security gateway only forwards the query to
name servers associated with that domain. If no match occurs, the security gateway
sequentially forwards the query to the specified static DNS servers. If no static DNS servers
exist, queries go to Internet name servers. Note that once static DNS servers are added,
Internet root name servers are no longer referenced.
