39-2
Software Configuration Guide—Release 15.0(2)SG
OL-23818-01
Chapter 39 Configuring Private VLANs
About Private VLANs
Purpose of a PVLAN
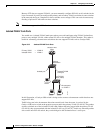
Using PVLANs provides scalability and IP address management benefits for service providers and
Layer 2 security for customers. PVLANs partition a regular VLAN domain into subdomains. A
subdomain is represented by a pair of VLANs: a primary VLAN and a secondary VLAN. A PVLAN can
have multiple VLAN pairs, one pair for each subdomain. All VLAN pairs in a PVLAN share the same
primary VLAN. The secondary VLAN ID differentiates one subdomain from another. See Figure 39-1.
Figure 39-1 Private-VLAN Domain
The three types of secondary VLANs are as follows:
• Isolated VLANs—Ports within an isolated VLAN cannot communicate with each other at the
Layer 2 level.
• Community VLANs—Ports within a community VLAN can communicate with each other but
cannot communicate with ports in other communities at the Layer 2 level.
• Twoway-Community VLANs—Bidirectional VLAN. Ports within a twoway-community VLAN can
communicate with each other but not with communities or twoway-communities at the Layer 2 level.
Note Beginning with Cisco IOS Release 15.0(2)SG, you can use a twoway-community VLAN to
apply VACLs or QoS in both directions per-community and per-customer.
A promiscuous port can serve only one primary VLAN, one isolated VLAN, and multiple community
(or twoway-community) VLANs. Layer 3 gateways are typically connected to the switch through a
promiscuous port.
208744
Private
Private
VLAN
VLAN
domain
domain
Private
VLAN
domain
Primary
VLAN
SubdomainSubdomain
Secondary
community VLAN
SubdomainSubdomain
Secondary
community VLAN
Secondary
isolated VLAN or
Twoway-Community
VLAN
Secondary
isolated VLAN or
Twoway-Community
VLAN