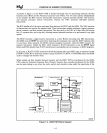
OVERVIEW OF NUMERIC PROCESSING
A
few
examples, which
show
how
the 80287 might be used in specific numerics applications, are
described below. In many cases, these types of systems have been implemented
in
the past with
minicomputers. The advent of the
80287 brings the size and cost savings of microprocessor technology
to these applications for the first time.
• Business data processing-The NPX's ability
to
accept decimal operands and produce exact decimal
results of up to
18
digits greatly simplifies accounting programming. Financial calculations
that
use
power functions can take advantage of the 80287's exponentiation and logarithmic instructions.
Process
control-The
80287 solves dynamic range problems automatically, and its extended preci-
sion allows control functions to be fine-tuned
for
more accurate and efficient performance. Control
algorithms implemented with the
NPX
also contribute
to
improved reliability and safety, while the
80287's speed can be exploited in real-time operations.
Computer numerical control
(CNC)-The
80287 can move and position machine tool heads with
accuracy in real-time. Axis positioning
also
benefits from the hardware trigonometric support provided
by the 80287.
Robotics-Coupling
small size and modest power requirements with powerful computational abili-
ties, the
NPX
is
ideal for on-board six-axis positioning.
Navigation-Very
small, lightweight, and accurate inertial guidance systems can be implemented
with the 80287. Its built-in trigonometric functions can speed and simplify the calculation of position
from bearing data.
• Graphics
terminals-The
80287 can be used in graphics terminals
to
locally perform many functions
that normally demand the attention of a main computer; these include rotation, scaling, and inter-
polation.
By
also using an 82720 Graphics Display Controller to perform high speed data transfers,
very powerful and highly self-sufficient terminals can be built from a relatively small number of
80286 family parts.
Data
acquisition-The
80287 can be used to scan, scale, and reduce large quantities of data
as
it
is
collected, thereby lowering storage requirements and time required to process the data for analysis.
The preceding examples are oriented toward
traditional numerics applications. There are, in addition,
many other types of systems that
do
not appear to the end user
as
computational, but can employ the
80287 to advantage. Indeed, the 80287 presents the imaginative system designer with an opportunity
similar to that created by the introduction of the microprocessor itself. Many applications can be viewed
as numerically-based if sufficient computational power
is
available
to
support this
view.
This
is
analo-
gous to the thousands of successful products that have been built around
"buried" microprocessors,
even though the products themselves bear little resemblance to computers.
Upgradability
The architecture of the 80286
CPU
is
specifically adapted to allow easy upgradability to use an 80287,
simply by plugging in the
80287 NPX. For this reason, designers of 80286 systems may wish to incor-
porate the
80287
NPX
into their designs in order to offer two levels of price and performance at little
2dditi0!!~!
GOSt.
Two features of the 80286
CPU
make the design and support of upgradable 80286 systems particularly
simple:
• The 80286 can be programmed to recognize the presence of an 80287 NPX;
that
is,
software can
recognize whether it
is
running
on
an 80286 or an 80287 system.
After determining whether the
80287
NPX
is
available, the 80286
CPU
can be instructed
to
let the
NPX
execute all numeric instructions.
If
an 80287
NPX
is
not available, the 80286
CPU
can emulate
1-4