Reference Manual for the ProSafe Wireless 802.11g Firewall/Print Server Model FWG114P v2
Virtual Private Networking F-5
201-10301-02, May 2005
Mode
SAs operate using modes. A mode is the method in which the IPSec protocol is applied to the
packet. IPSec can be used in tunnel mode or transport mode. Typically, the tunnel mode is used for
gateway-to-gateway IPSec tunnel protection, while transport mode is used for host-to-host IPSec
tunnel protection. A gateway is a device that monitors and manages incoming and outgoing
network traffic and routes the traffic accordingly. A host is a device that sends and receives
network traffic.
• Transport Mode: The transport mode IPSec implementation encapsulates only the packet’s
payload. The IP header is not changed. After the packet is processed with IPSec, the new IP
packet contains the old IP header (with the source and destination IP addresses unchanged)
and the processed packet payload. Transport mode does not shield the information in the IP
header; therefore, an attacker can learn where the packet is coming from and where it is going
to. The previous packet diagrams show a packet in transport mode.
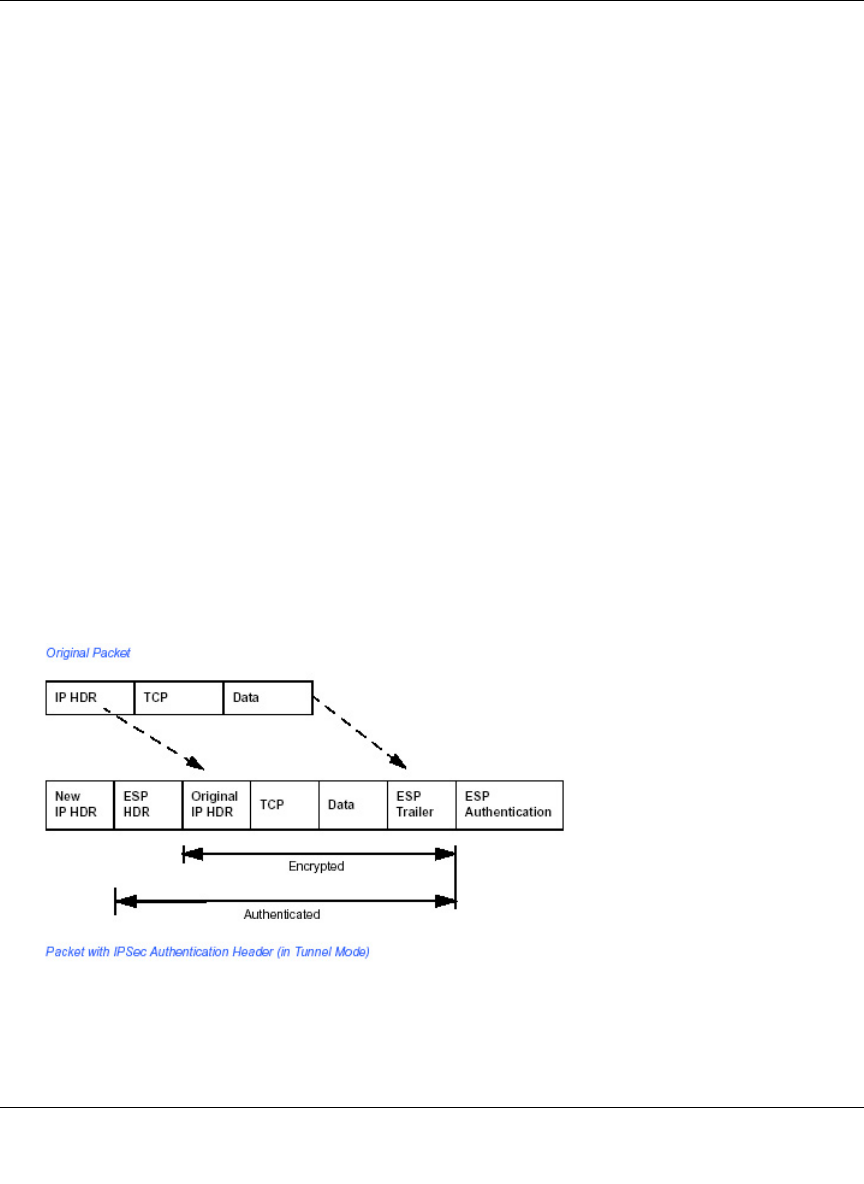
• Tunnel Mode: The tunnel mode IPSec implementation encapsulates the entire IP packet. The
entire packet becomes the payload of the packet that is processed with IPSec. A new IP header
is created that contains the two IPSec gateway addresses. The gateways perform the
encapsulation/decapsulation on behalf of the hosts. Tunnel mode ESP prevents an attacker
from analyzing the data and deciphering it, as well as knowing who the packet is from and
where it is going.
Note: AH and ESP can be used in both transport mode or tunnel mode.
Figure F-3: Original packet and packet with IPSec ESP in Tunnel mode


















