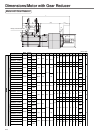
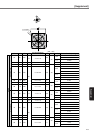
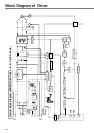
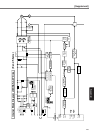
227
[Supplement]
Supplement
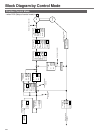
Function
Real time
Normal mode
Hardware error
Software error
Protection
function
External scale division
gradual increase
setting range
Instantaneous
speed observer
Division function of
encoder feedback pulse
Unnecessary wiring
mask function
Alarm data trace back function
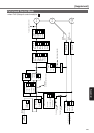
The number of points
Homing
operation
Jog operation
Step operation
Block operation
Continuous block
operation
A function to reduce vibration by removing the vibration frequency component
when the front end of the machine vibrates.
Ratio between the encoder pulse (numerator) and the external scale pulse (denominator)
can be set within the setting range : (1 to 10000 x 2
(0–17)
)/(1 to 10000)
maximum 60 points
Eight types of homing operations
[home sensor + Z phase (based on the front end), home sensor (based on the front end),
home sensor + Z phase (based on the rear end), limit sensor + Z phase, limit sensor,
Z phase homing, Bumping homing, and data set]
The motor can be moved in a positive direction or negative direction independently.
This is useful for teaching or adjustment.
A point number increments by 1 automatically whenever an operation command is given.
A step operation can be performed easily only by turning the STB signal on/off.
You can operate the motor actually using this console,
set a target position and execute some test operations.
Load inertia is determined at real time in the state of actual operation
and gain corresponding to the rigidity is set automatically.
Load inertia is determined by driving the equipment with operation command
within the driver and gain corresponding to the rigidity is set automatically.
Available only for position control.
A function to improve the speed detection accuracy,
achieve the quick response and, at the same time,
reduce the vibration at the stop by estimating the motor speed using a load model.
The following control input signal can be masked:
CW over-travel inhibit, CCW over-travel inhibit, multi function input1 and 2 ,
point specifying input(P8-IN,P16-IN,P32-IN), Servo-ON
The number of pulses can be set up arbitrarily. (at the maximum encoder pulse)
Overload, undervoltage, overspeed, overload, overheat, over current, encoder error, etc.
Large positional deviation, Undefined data error , EEPROM error, etc.
Traceable up to 14 alarm data including present alarm data.
The most basic operation. Specify a point number set in advance when performing the operation.
The four types of modes [incremental operation, absolute operation,
rotary axis operation and dwell timer (waiting time)]
Combined block
operation
Sequential
Operation
Teaching
(Console (option)
is necessary)
Damping Control
Operation modeAuto tuning
Several step operations can be performed continuously.
Once an operation starts, the operation continues to a specified point number.
A step operation is performed according to combined several point numbers.
This is useful when you want to change the speed during a step operation.