Rev.1.02 Jul 01, 2005 page 237 of 314
REJ09B0126-0102
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NL, M16C/6NN) 20. Flash Memory Version
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
20.1.1 Boot Mode
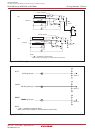
The microcomputer enters boot mode when a hardware reset occurs while an “H ” signal is applied to the
CNVSS and P5_0 pins and an “L ” signal is applied to the P5_5 pin. A program in the boot ROM area is
executed.
In boot mode, the FMR05 bit in the FMR0 register selects access to the boot ROM area or the user ROM
area.
The rewrite control program for standard serial I/O mode is stored in the boot ROM area before shipment.
The boot ROM area can be rewritten in parallel I/O mode only. If any rewrite control program using erase-write
mode (EW0 mode) is written in the boot ROM area, the flash memory can be rewritten according to the
system implemented.
20.2 Functions to Prevent Flash Memory from Rewriting
The flash memory has a built-in ROM code protect function for parallel I/O mode and a built-in ID code
check function for standard serial I/O mode and CAN I/O mode to prevent the flash memory from reading or
rewriting.
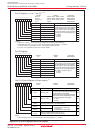
20.2.1 ROM Code Protect Function
The ROM code protect function inhibits the flash memory from being read or rewritten during parallel I/O
mode. Figure 20.2 shows the ROMCP register. The ROMCP register is located in the user ROM area.
The ROM code protect function is enabled when the ROMCR bits are set to other than “11b ”. In this case,
set the bit 5 to bit 0 to “111111b ”.
When exiting ROM code protect, erase the block including the ROMCP register by the CPU rewrite mode
or the standard serial I/O mode or CAN I/O mode.
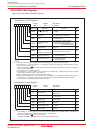
20.2.2 ID Code Check Function
Use the ID code check function in standard serial I/O mode and CAN I/O mode. The ID code sent from the
serial programmer is compared with the ID code written in the flash memory for a match. If the ID codes
do not match, commands sent from the serial programmer are not accepted. However, if the four bytes of
the reset vector are “FFFFFFFFh”, ID codes are not compared, allowing all commands to be accepted.
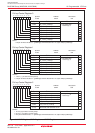
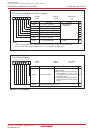
The ID codes are 7-byte data stored consecutively, starting with the first byte, into addresses 0FFFDFh,
0FFFE3h, 0FFFEBh, 0FFFEFh, 0FFFF3h, 0FFFF7h, and 0FFFFBh. The flash memory must have a
program with the ID codes set in these addresses.
Figure 20.3 shows the ID code store addresses.