Rev.1.02 Jul 01, 2005 page 299 of 314
REJ09B0126-0102
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NL, M16C/6NN) 22. Usage Precaution
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
22.13 CAN Module
22.13.1 Reading C0STR Register
The CAN module on the M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NL, M16C/6NN) updates the status of the C0STR
register in a certain period. When the CPU and the CAN module access to the C0STR register at the
same time, the CPU has the access priority; the access from the CAN module is disabled. Consequently,
when the updating period of the CAN module matches the access period from the CPU, the status of the
CAN module cannot be updated. (See Figure 22.5 When Updating Period of CAN Module Matches
Access Period from CPU.)
Accordingly, be careful about the following points so that the access period from the CPU should not
match the updating period of the CAN module:
(a) There should be a wait time of 3fCAN or longer (see Table 22.3 CAN Module Status Updating Period)
before the CPU reads the C0STR register. (See Figure 22.6 With a Wait Time of 3fCAN Before
CPU Read.)
(b) When the CPU polls the C0STR register, the polling period must be 3fCAN or longer. (See Figure 22.7
When Polling Period of CPU is 3fCAN or Longer.)
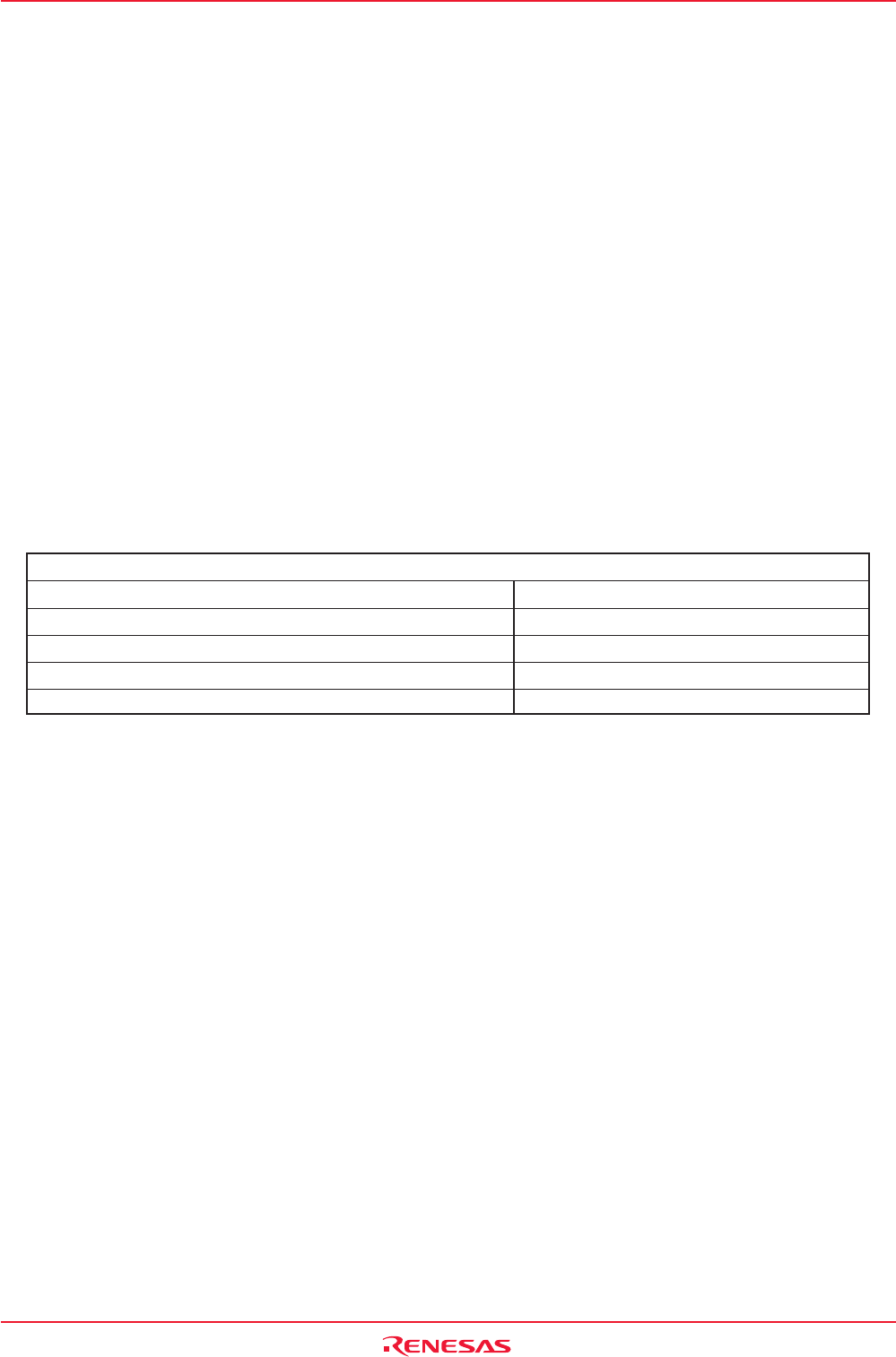
Table 22.3 CAN Module Status Updating Period
3fCAN Period = 3 ✕ XIN (Original Oscillation Period) ✕ Division Value of CAN Clock (CCLK)
(Example 1) Condition XIN 16 MHz CCLK: Divided by 1 3fCAN period = 3 ✕ 62.5 ns ✕ 1 = 187.5 ns
(Example 2) Condition XIN 16 MHz CCLK: Divided by 2 3fCAN period = 3 ✕ 62.5 ns ✕ 2 = 375 ns
(Example 3) Condition XIN 16 MHz CCLK: Divided by 4 3fCAN period = 3 ✕ 62.5 ns ✕ 4 = 750 ns
(Example 4) Condition XIN 16 MHz CCLK: Divided by 8 3fCAN period = 3 ✕ 62.5 ns ✕ 8 = 1.5 µs
(Example 5) Condition XIN 16 MHz CCLK: Divided by 16 3fCAN period = 3 ✕ 62.5 ns ✕ 16 = 3 µs
