Rev.1.02 Jul 01, 2005 page 76 of 314
REJ09B0126-0102
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NL, M16C/6NN) 10. Watchdog Timer
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
10. Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer is the function of detecting when the program is out of control. Therefore, we recommend
using the watchdog timer to improve reliability of a system. The watchdog timer contains a 15-bit counter
which counts down the clock derived by dividing the CPU clock using the prescaler. Whether to generate a
watchdog timer interrupt request or apply a watchdog timer reset as an operation to be performed when the
watchdog timer underflows after reaching the terminal count can be selected using the PM12 bit in the PM1
register. The PM12 bit can only be set to “1” (watchdog timer reset). Once this bit is set to “1”, it cannot be set
to “0” (watchdog timer interrupt) in a program. Refer to 5.3 Watchdog Timer Reset for details about watchdog
timer reset.
When the main clock, on-chip oscillator clock or PLL clock is selected for CPU clock, the divide-by-n value for
the prescaler can be selected to be 16 or 128. If a sub clock is selected for CPU clock, the divide-by-n value
for the prescaler is always 2 no matter how the WDC7 bit is set. The period of watchdog timer can be
calculated as given below. The period of watchdog timer is, however, subject to an error due to the prescaler.
For example, when CPU clock = 16 MHz and the divide-by-n value for the prescaler = 16, the watchdog timer
period is approx. 32.8 ms.
The watchdog timer is initialized by writing to the WDTS register. The prescaler is initialized after reset. Note
that the watchdog timer and the prescaler both are inactive after reset, so that the watchdog timer is
activated to start counting by writing to the WDTS register.
In stop mode, wait mode and hold state, the watchdog timer and prescaler are stopped. Counting is
resumed from the held value when the modes or state are released.
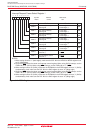
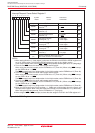
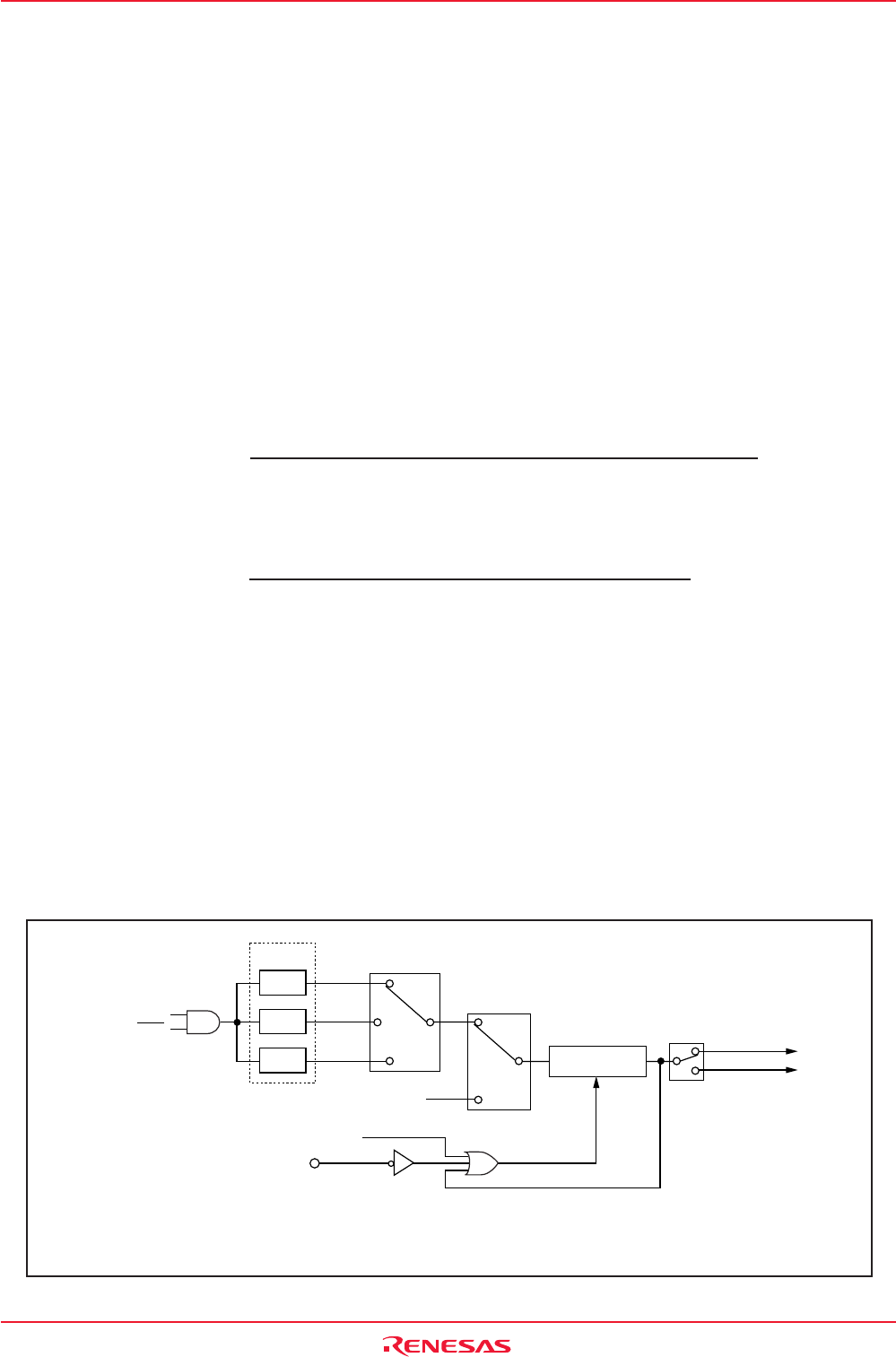
Figure 10.1 shows the block diagram of the watchdog timer. Figure 10.2 shows the watchdog timer-related
registers.
With main clock, on-chip oscillator clock or PLL clock selected for CPU clock
Watchdog timer period =
Prescaler dividing (16 or 128) ✕ Watchdog timer count (32768)
CPU clock
With sub clock selected for CPU clock
Watchdog timer period =
Prescaler dividing (2) ✕ Watchdog timer count (32768)
CPU clock
Figure 10.1 Watchdog Timer Block Diagram
1/16
CM07 = 0
WDC7 = 0
PM22 = 0
PM22 = 1
Set to
"7FFFh"
On-chip oscillator clock
Write to WDTS register
Internal RESET signal
("L" active)
PM12 = 0
Watchdog timer
Interrupt request
PM12 = 1
Watchdog timer
Reset
CPU clock
HOLD
CM07 = 0
WDC7 = 1
CM07 = 1
Prescaler
1/128
1/2
Watchdog timer
CM07 : Bit in CM0 register
WDC7: Bit in WDC register
PM12 : Bit in PM1 register
PM22 : Bit in PM2 register