Noise gating
Frequently, low-level signals become noise when a file’s bit depth is decreased. For this reason, it is preferable to have complete silence
between sounds in an audio file.
1.
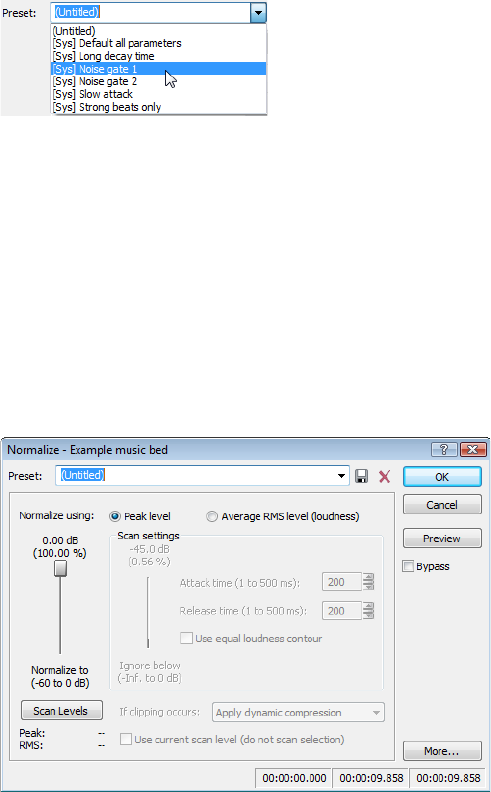
From the Effects menu, choose Noise Gate. The Noise Gate dialog appears
2.
Choose a noise gate preset from the Preset drop-down list and click OK. A noise gate is applied to the audio, negating its low-level
signals.
Compressing
Decreasing the dynamic range of a sound file makes it easier to represent with decreased bit depth.
1.
From the Effects menu, choose Dynamics, and choose Graphic from the submenu. The Graphic Dynamics dialog appears.
2.
Choose a preset with a small amount of compression (2:1 or less) from the Preset drop-down list and click OK.
Normalizing
Normalizing a file prior to decreasing its bit depth ensures that the entire dynamic range is used. In addition, normalization lowers the
signal-to-noise ratio.
1.
From the Process menu, choose Normalize. The Normalize dialog appears.
2.
Select the Peak level radio button.
3.
Set the Normalize to fader to 0 dB (peak) and click OK.
Applying compression and normalization simultaneously
1.
From the Process menu, choose Normalize. The Normalize dialog appears.
2.
Select the Average RMS level radio button.
3.
Choose Apply dynamic compression in the If clipping occurs drop-down list and click OK.
104
| CHAPTER 5
