Appendix B
Printer Communications Interface Technical Information
System Considerations
Communications Code — The printer sends and receives American Standard Code for Information
Interchange (ASCII). This code consists of 128 characters (256 for Code Page 850) including upper-
and lower-case letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and various control codes.
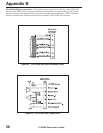
Interfaces — The method of interfacing the printer to a data source depends on the communication
options installed in the printer and the host. The standard interfaces are an RS-232/RS-422/RS-485
serial data port and a Centronics-compatible parallel port. Optional IBM Twinax, IBM Coax and
Ethernet options are available for those applications which require them.
Data Specifications — When communicating via an asynchronous serial data port (RS-232/RS-422/
RS-485), the baud rate, number of data and stop bits, the parity, and the XON/XOFF or DTR control
are user-selectable and should be set to match those of the host computer. When communicating via
the Centronics-compatible parallel port, the previously mentioned parameters are not considered.
Refer to “Configuration and Calibration” to configure the communication parameters for the printer.
Interface Considerations
RS-232 – A serial communication method consisting of data and control signals; available as a
standard feature on most PCs and other hosts.
Advantages: Cables and connectors are readily available from computer equipment stores and
suppliers; easy to connect; two-way communication between the host and the printer.
Disadvantages: Slower than the parallel connection; limited to 50 feet (15.24 meters) of cable.
RS-422 – A single-user current loop serial communication method.
Advantages: Longer cable length up to 4000 feet (1219.2 m); greater immunity to data corruption
caused by industrial motors and fluorescent lights; two-way communication between the host and the
printer.
Disadvantages: Not commonly available on standard PCs without additional hardware; slower than
the parallel connection.
RS-485 – A multiple-user current loop serial communication method that is used to support multiple
printers connected to a single host.
Advantages: Longer cable length up to 4000 feet (1219.2 m); greater immunity to data corruption
caused by industrial motors and fluorescent lights; two-way communication between the host and the
printer.
Disadvantages: Not commonly available on standard PCs without additional hardware; slower than
the parallel connection.
Centronics-compatible Parallel – This is a common communication method available on most PCs
and other hosts.
Advantages: Fastest of the four communication interfaces; cables and connectors are readily
available from computer equipment stores and suppliers; easy to connect.
Disadvantages: One-way communication (the serial port is used to send printer status to the host);
shorter recommended cable length of 6 feet (1.83 m).
170PAX2-Series User’s Guide
55