BLADEOS 6.5.2 Application Guide
142 Chapter 9: Quality of Service BMD00220, October 2010
Using 802.1p Priority to Provide QoS
The G8124 provides Quality of Service functions based on the priority bits in a packet’s VLAN
header. (The priority bits are defined by the 802.1p standard within the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
header.) The 802.1p bits, if present in the packet, specify the priority that should be given to packets
during forwarding. Packets with a numerically higher (non-zero) priority are given forwarding
preference over packets with lower priority value.
The IEEE 802.1p standard uses eight levels of priority (0-7). Priority 7 is assigned to highest
priority network traffic, such as OSPF or RIP routing table updates, priorities 5-6 are assigned to
delay-sensitive applications such as voice and video, and lower priorities are assigned to standard
applications. A value of 0 (zero) indicates a “best effort” traffic prioritization, and this is the default
when traffic priority has not been configured on your network. The switch can filter packets based
on the 802.1p values.
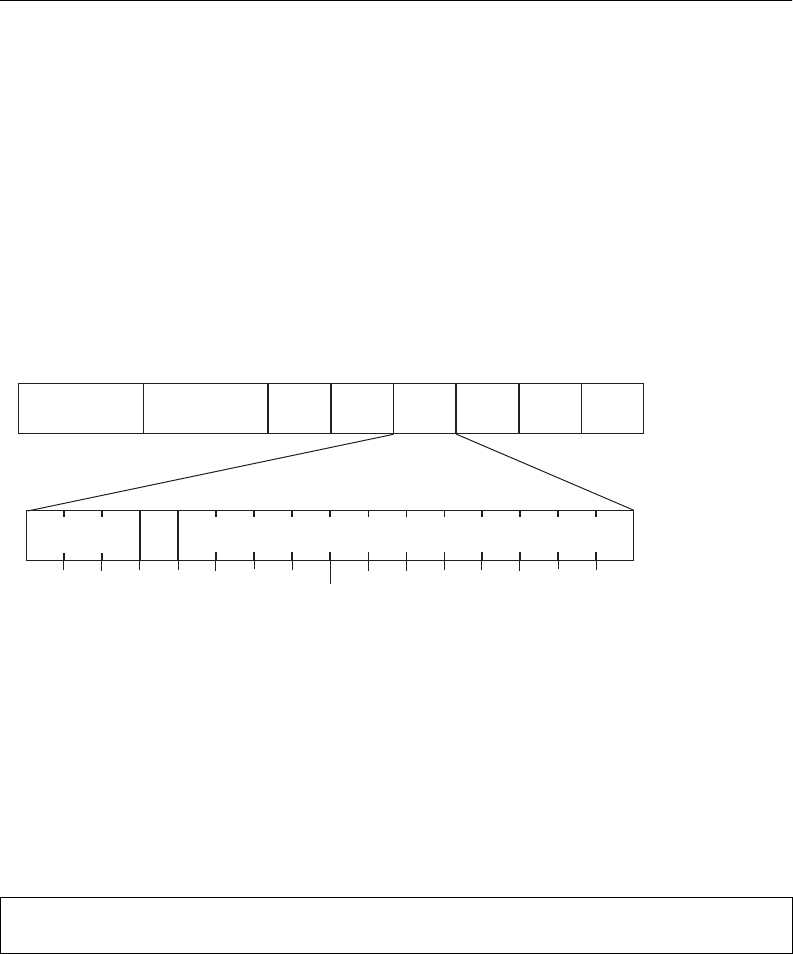
Figure 16 Layer 2 802.1q/802.1p VLAN tagged packet
Ingress packets receive a priority value, as follows:
Tagged packets—switch reads the 802.1p priority in the VLAN tag.
Untagged packets—switch tags the packet and assigns an 802.1p priority value, based on the
port’s default 802.1p priority.
Egress packets are placed in a COS queue based on the priority value, and scheduled for
transmission based on theCOS queue number. Higher COS queue numbers provide forwarding
precedence.
To configure a port’s default 802.1p priority value, use the following commands.
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Priority
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
VLAN Identifier (VID)
SFD
DMAC
SMAC Tag
E Type
Data
FCS
Preamble
RS G8124(config)# interface port 1
RS G8124(config-if)# dot1p <802.1p value (0-7)>


















