22-7
Cisco BPX 8600 Series Installation and Configuration
Release 9.3.10, Part Number 78-11603-01 Rev. D0, July 2001
Chapter 22 Configuring Frame Relay to ATM Network and Service Interworking
ATM Protocol Stack
DiscardselectionisbaseduponthestandardCLPbitinthecells.WhentheroutingpathentersanIGX
switch, a BTM card that supports Interworking traffic is required to convert the connection data from
cells to frames (frames to fastpackets out onto MuxBus to FRP/cell bus to FRM), and visa versa.
Additionally, the AAL-5 framing is removed upon conversion to frames, and added upon conversion to
cells. At the destination (FRM), FastPackets are placed in the port queue and, when a complete frame
has been assembled, the frame is played out the remote port in the original format (as provided in the
frames delivered inside AAL-5 PDUs).
For each connection, only a single dlci can be played out for all traffic exiting the port, and is inserted
into the frame headers. The standard LAPD framing format is played out the port on the FRM.
At the FRM card, several additional protocol mappings take place. First, the Interworking Unit acts as
a pseudo endpoint for the purposes of ATM for all constructs that have no direct mapping into Frame
Relay, such as loopbacks and FERF indications. Thus, end-to-end loopback OAM cells that ingress to
FRM cards from the network are returned to the ATM network without allowing them to proceed into
the Frame Relay network, which has no equivalent message construct. Further, AIS and supervisory
cells and FastPackets (from the Frame Relay direction) are converted into their counterparts within the
other network.
ATM Protocol Stack
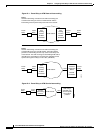
A general view of the ATM protocol layers with respect to the Open Systems Interconnection model is
shown in Figure 22-7. In this example, a large frame might be input into the top of the stacks. Each layer
performs a specific function before passing it to the layer below. A protocol data unit (PDU) is the name
of the data passed down from one layer to another and is the Service Data Unit (SDU) of the layer below
it.
For Frame Relay to ATM interworking, a specific convergent sublayer, Frame Relay Service Specific
Convergent Sublayer, FR-SSCS is defined. This is also referred to as FR-CS, in shortened notation.
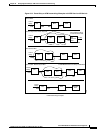
Figure 22-7 ATM Layers
Higher layer functions
Convergence sublayer
(CS)
Physical
layer
SAR
ATM layer
TC
PM
AALs
(ATM
adaptation
layers)
Management plane
Control plane User plane
Service specific, e.g., FR-SSCS
Common part convergence
sublayer CPCS
Segmentation and reassembly
Cell header insert/extract
Cell multiplexing/demultiplexing
VPI/VCI addressing and translation
Generic flow control
Transmission convergence
Physical medium
H8021