24-21
Cisco BPX 8600 Series Installation and Configuration
Release 9.3.10, Part Number 78-11603-01 Rev. D0, July 2001
Chapter 24 Configuring BXM Virtual Trunks
Command Overview
Configuration with cnfrsrc
Use cnfrsrc to configure conids (lcns) and bandwidth. The conid capacity indicates the number of
connection channels on the trunk port which are usable by the virtual trunk.
This number cannot be greater than the total number of connection channels on the card. The maximum
number of channels is additionally limited by the number of VCI bits in the UNI cell header.
For a virtual trunk, the number is divided by the maximum number of virtual trunks on the port to
determine the default. You configure this value by using the cnfsrc command on the BPX.
Table 24-8 lists the number of connection ids for virtual trunks on various cards.
Configuration with cnftrkparm
cnftrkparm
BXM and UXM virtual trunks have all the configuration parameters for queues as physical trunks.
The integrated alarm thresholds for major alarms and the gateway efficiency factor is the same for all
virtual trunks on the port.
Note that BNI VTS are supported by a single queue and do not support configuration of all the
OptiClass queues on a single virtual trunk.
When a physical port attribute change is made, you are notified that all trunks on the port are affected.
APS Redundancy
Virtual trunks support APS redundancy on BXM OC-3 and OC-12 ports. For more information, refer
to the section on APS Redundancy in this manual. You configure this by using primarily these
commands:
• addapsln
• delapsln
• switchapsln
• cnfapsln
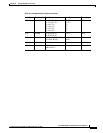
Table 24-7 VPI Ranges
Port Type Valid VPI Range
BXM/UXM (UNI) 1–255
BXM/UXM (NNI) 1–4095
BNI T3/E3 1–255
BNI OC-3 1–63
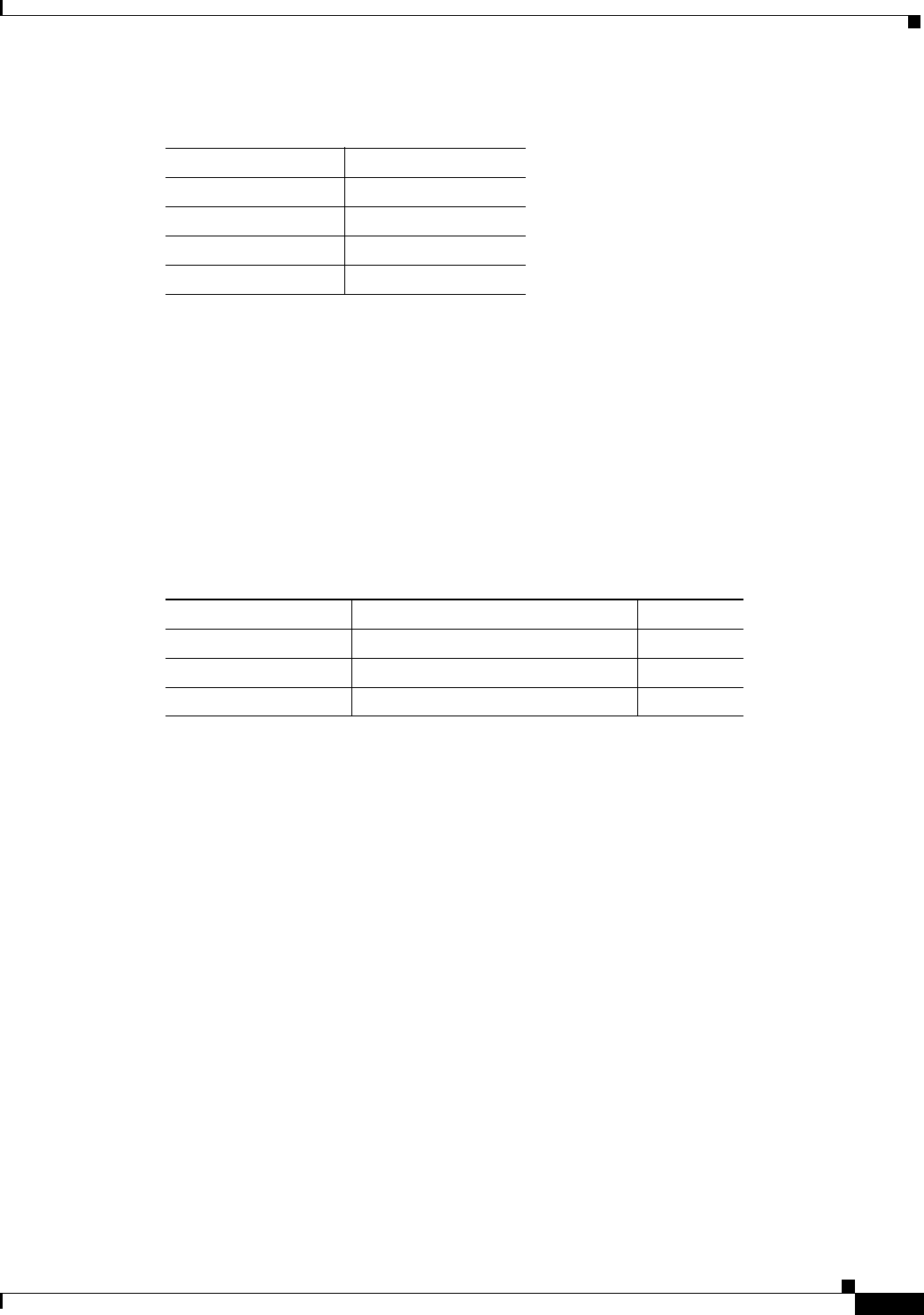
Table 24-8 Maximum Connection IDs (LCNs)
Port Type Maximum Conids Default
BXM/UXM 1–(number of channels on the card) 256
BNI T3/E3 1–1771 256
BNI OC-3 1–15867 (3837 max/vtrk 256