4-2
Cisco uBR7200 Series Universal Broadband Router Software Configuration Guide
OL-2239-03
Chapter4 Configuring DOCSIS Baseline Privacy Interface on the Cisco uBR7200 Series
Baseline Privacy Interface Overview
When BPI is operational, downstream multicast traffic flow that typically does not have a SID associated
with it, now has a SID. The Privacy Extended Header Element includes the SID associated with the MAC
Packet Data Physical Data Unit (PDU). The SID along with other components of the extended header
element identifies to a CM the keying material required to decrypt the MAC PDU’s packet data field.
BPI’s key management protocol runs between the CMTS and the CM. CMs use the protocol to obtain
authorization and traffic keying material relevant to a particular SID from the CMTS and to support
periodic reauthorization and key refresh.
The key management protocol uses RSA—a public key encryption algorithm—and the electronic
codebook (ECB) mode of DES to secure key exchanges between the CMTS and a CM. Privacy is in the
form of 56-bit (the default) or 40-bit encryption between the CMTS and CM. Since BPI is part of
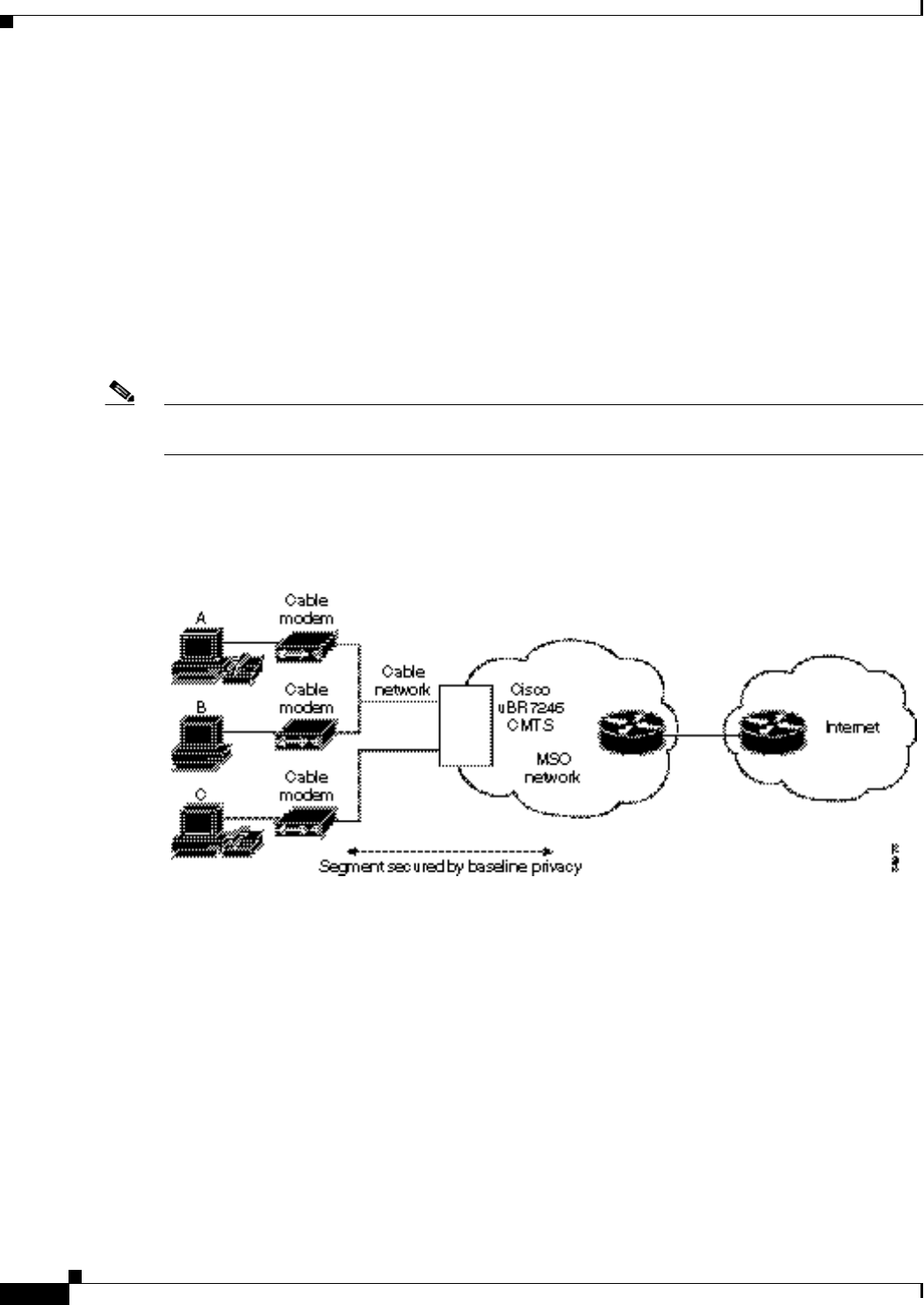
DOCSIS, all DOCSIS-certified CMs and qualified CMTS are fully interoperable. Figure4-1shows a BPI
architecture.
Note CMs must have factory-installed RSA private/public key pairs to support internal algorithms to generate
key pairs prior to first BPI establishment.
A SID’s keying material has a limited life span. When the CMTS delivers SID keying material to a CM,
it also provides the CM with the lifetime value.
Figure4-1 BPI Network Example
BPI Key Management
BPI initialization begins with the CM sending the CMTS an authorization request, containing data
identifying:
• CM—48-bit IEEE MAC address
• CM’s RSA public key
• List of zero or more assigned unicast SIDs that have been configured to run BPI
At that time, BPI provides basic protection against theft of service by ensuring the CM, identified by its
MAC address, can obtain keying materials only it is authorized to access. The CMTS replies with a list
of SIDs on which to run BPI. The reply also includes an authorization key from which the CM and CMTS
derive the keys needed to secure a CM’s subsequent requests for additional encryption keys. After
obtaining the traffic encryption key, the CMs begin to transmit encrypted data.


















