30
EMC Host Connectivity with QLogic FC and iSCSI HBAs and FCoE CNAs for the Linux Environment
Installation Steps
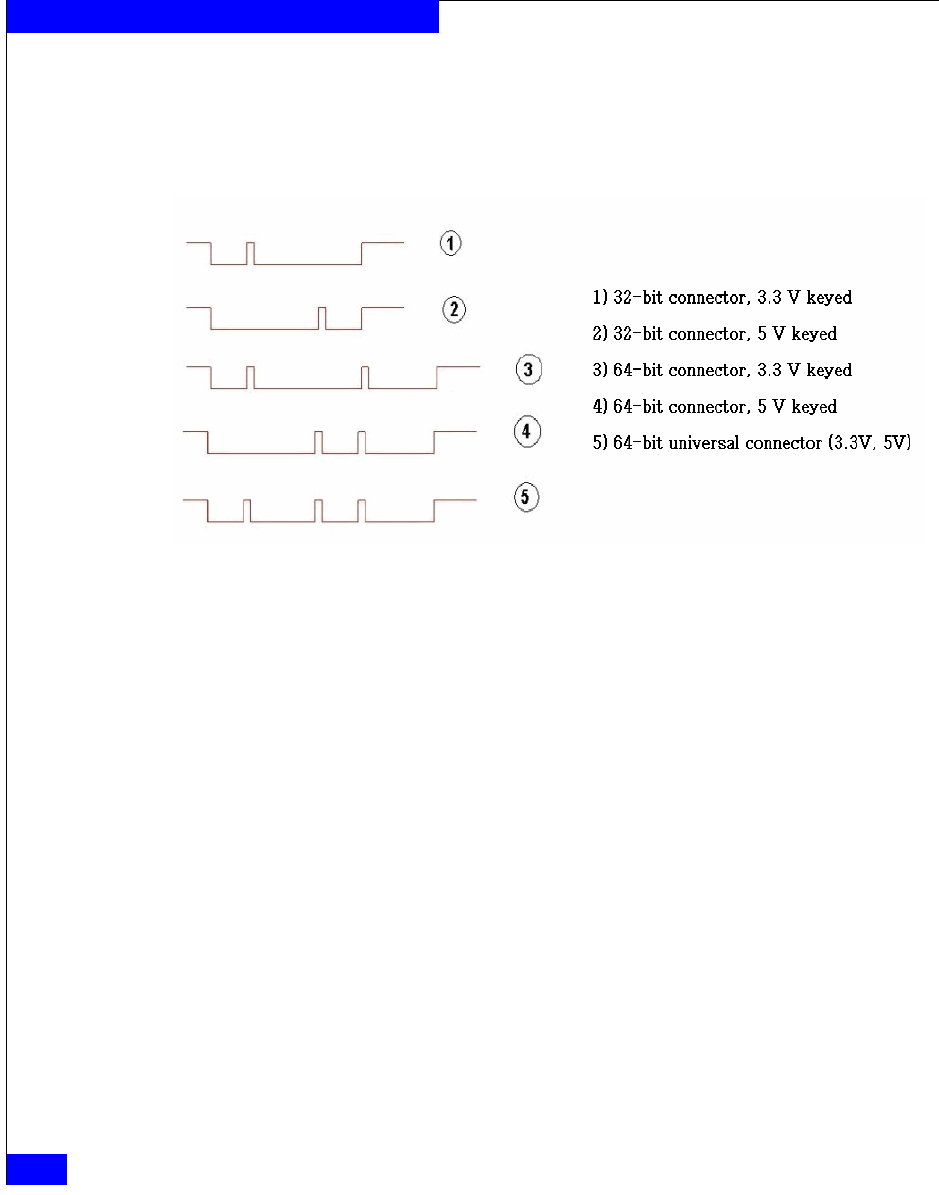
Figure 3 shows the adapter edge connectors compatible with the PCI
slots shown in Figure 2 on page 29. Note adapter 5, which shows a
universal adapter edge connector. Universal adapters are compatible
with both 3.3 V and 5 V PCI slots.
Figure 3 Adapter edge connectors
PCI-X (or PCI Extended) slots increase the speed with which data
travels over the bus. PCI-X slots appear identical to a 64-bit PCI slot
keyed for 3.3 V. (Refer to number 3 in Figure 2 on page 29 and
Figure 3.) PCI-X slots are backwards compatible with 3.3 V PCI
adapters and universal adapters. Inserting standard PCI adapters
into PCI-X slots will lower the bus speed as they cannot take
advantage of the improved performance.
PCI-X 2.0 is the next generation of PCI-X buses. PCI-X 2.0 increases
the bus speed again, providing more performance for adapters.
PCI-X 2.0 slots also appear identical to a 64-bit PCI slot keyed for 3.3
V. (Refer to number 3 in Figure 2 and Figure 3.) PCI-X 2.0 is also fully
backward compatible with 3.3 V PCI and PCI-X.
PCI Express (sometimes noted as PCIe) is a new bus type that uses
the existing PCI model, but implements it in a faster, serial protocol.
Because of the serial way it transmits data, the PCI Express bus slot
can be different sizes depending on the throughput it supports. PCI
Express slot speeds are expressed in "lanes" and are normally shown
as x1, x4, x8, and x16. Each type of slot is a different length (as shown
in Figure 4 on page 31) and adapter edge connectors will also be of
varying lengths depending on how many lanes they require for


















