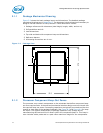
Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 11
Introduction
§
T
CASE
_
MAX
The maximum case temperature as specified in a component specification.
TCC Thermal Control Circuit: Thermal monitor uses the TCC to reduce the die temperature by using clock
modulation and/or operating frequency and input voltage adjustment when the die temperature is very
near its operating limits.
T
CONTROL
Tcontrol is a static value that is below the TCC activation temperature and used as a trigger point for fan
speed control. When DTS > Tcontrol, the processor must comply to the TTV thermal profile.
TDP Thermal Design Power: Thermal solution should be designed to dissipate this target power level. TDP is not
the maximum power that the processor can dissipate.
Thermal Monitor A power reduction feature designed to decrease temperature after the processor has reached its maximum
operating temperature.
Thermal Profile Line that defines case temperature specification of the TTV at a given power level.
TIM Thermal Interface Material: The thermally conductive compound between the heatsink and the processor
case. This material fills the air gaps and voids, and enhances the transfer of the heat from the processor
case to the heatsink.
TTV Thermal Test Vehicle. A mechanically equivalent package that contains a resistive heater in the die to
evaluate thermal solutions.
T
LA
The measured ambient temperature locally surrounding the processor. The ambient temperature should be
measured just upstream of a passive heatsink or at the fan inlet for an active heatsink.
T
SA
The system ambient air temperature external to a system chassis. This temperature is usually measured
at the chassis air inlets.
Table 1-2. Terms and Descriptions (Sheet 2 of 2)
Term Description