Thermal/Mechanical Specifications and Design Guidelines 67
Sensor Based Thermal Specification Design Guidance
8.2 Sensor Based Thermal Specification
The sensor based thermal specification consists of two parts. The first is a thermal
profile that defines the maximum TTV T
CASE
as a function of TTV power dissipation. The
thermal profile defines the boundary conditions for validation of the thermal solution.
The second part is a defined thermal solution performance (Ψ
CA
) as a function of the
DTS value as reported over the PECI bus when DTS is greater than T
CONTROL
. This
defines the operational limits for the processor using the TTV validated thermal
solution.
8.2.1 TTV Thermal Profile
For the sensor based specification, the only reference made to a case temperature
measurement is on the TTV. Functional thermal validation will not require the user to
apply a thermocouple to the processor package or measure processor power.
Note: All functional compliance testing will be based on fan speed response to the reported
DTS values above T
CONTROL
. As a result, no conversion of TTV T
CASE
to processor T
CASE
will be necessary.
A knowledge of the system boundary conditions is necessary to perform the heatsink
validation. Section 8.3.1 will provide more detail on defining the boundary conditions.
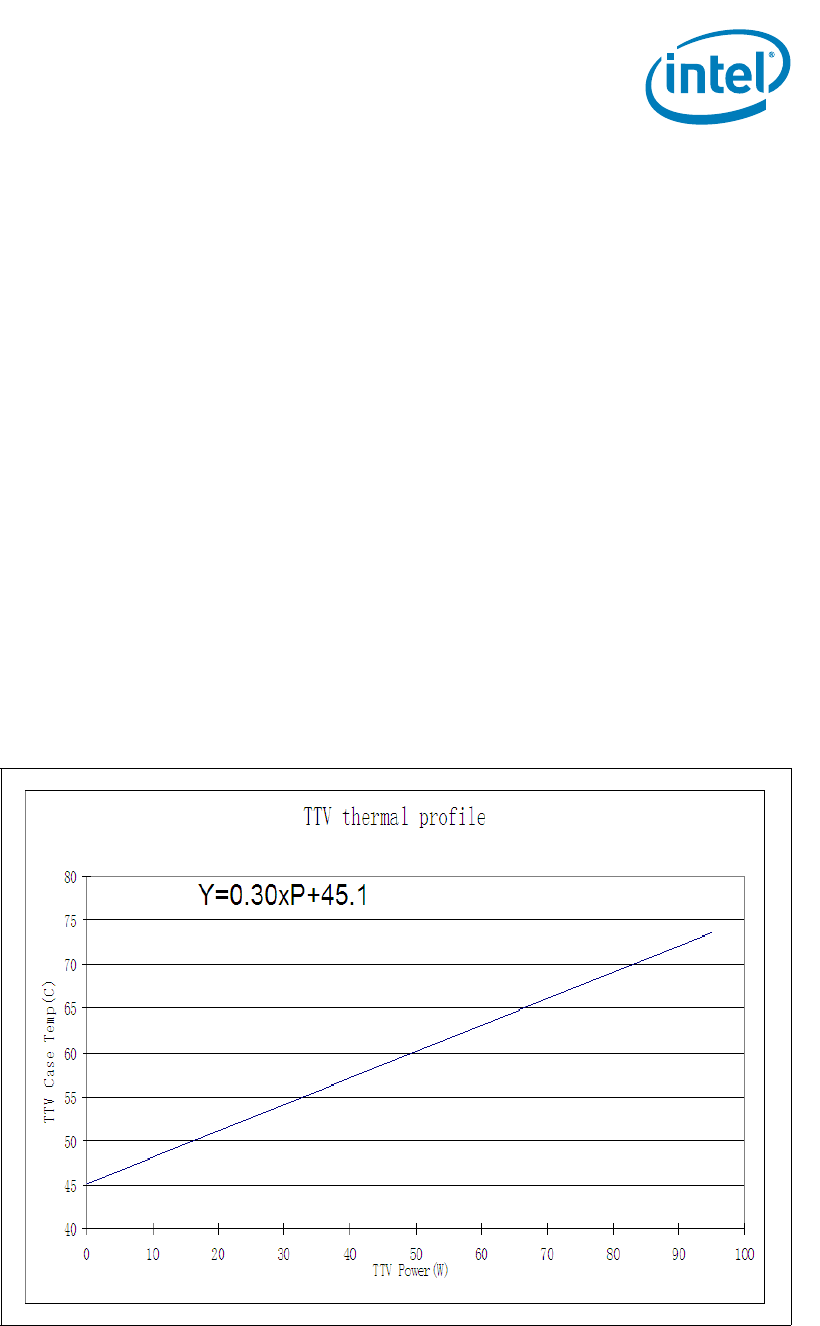
The TTV is placed in the socket and powered to the recommended value to simulate the
TDP condition. See Figure 8-2 for an example of the Intel
®
Xeon
®
processor E3-1280
(95W) TTV thermal profile.
Figure 8-2. Intel
®
Xeon
®
Processor E3-1280 (95W) TTV Thermal Profile
